EAM_Dynamo_BonnyGrigorevTerentyev_2014EAM1_WHHe__MO_292520929154_000
EAM_Dynamo_BonnyGrigorevTerentyev_2014EAM1_WHHe__MO_292520929154_000
| Title
A single sentence description.
|
EAM potential (LAMMPS cubic hermite tabulation) for the W-H-He system developed by Bonny et al. (2014); Potential EAM1 v000 |
|---|---|
| Description
A short description of the Model describing its key features including for example: type of model (pair potential, 3-body potential, EAM, etc.), modeled species (Ac, Ag, ..., Zr), intended purpose, origin, and so on.
|
EAM potential for the W-H-He system developed by Bonny, Grigorev, and Terentyev (2014); Potential EAM1. In this work we developed an embedded atom method potential for large scale atomistic simulations in the ternary tungsten–hydrogen–helium (W–H–He) system, focusing on applications in the fusion research domain. Following available ab initio data, the potential reproduces key interactions between H, He and point defects in W and utilizes the most recent potential for matrix W. The potential is applied to assess the thermal stability of various H–He complexes of sizes too large for ab initio techniques. The results show that the dissociation of H–He clusters stabilized by vacancies will occur primarily by emission of hydrogen atoms and then by break-up of V–He complexes, indicating that H–He interaction does influence the release of hydrogen. |
| Species
The supported atomic species.
| H, He, W |
| Disclaimer
A statement of applicability provided by the contributor, informing users of the intended use of this KIM Item.
|
None |
| Content Origin | NIST IPRP (https://www.ctcms.nist.gov/potentials/W.html#W-H-He) |
| Contributor |
Ellad B. Tadmor |
| Maintainer |
Ellad B. Tadmor |
| Developer |
Giovanni Bonny Petr Grigorev D. Terentyev |
| Published on KIM | 2018 |
| How to Cite | Click here to download this citation in BibTeX format. |
| Citations
This panel presents information regarding the papers that have cited the interatomic potential (IP) whose page you are on. The OpenKIM machine learning based Deep Citation framework is used to determine whether the citing article actually used the IP in computations (denoted by "USED") or only provides it as a background citation (denoted by "NOT USED"). For more details on Deep Citation and how to work with this panel, click the documentation link at the top of the panel. The word cloud to the right is generated from the abstracts of IP principle source(s) (given below in "How to Cite") and the citing articles that were determined to have used the IP in order to provide users with a quick sense of the types of physical phenomena to which this IP is applied. The bar chart shows the number of articles that cited the IP per year. Each bar is divided into green (articles that USED the IP) and blue (articles that did NOT USE the IP). Users are encouraged to correct Deep Citation errors in determination by clicking the speech icon next to a citing article and providing updated information. This will be integrated into the next Deep Citation learning cycle, which occurs on a regular basis. OpenKIM acknowledges the support of the Allen Institute for AI through the Semantic Scholar project for providing citation information and full text of articles when available, which are used to train the Deep Citation ML algorithm. |
This panel provides information on past usage of this interatomic potential (IP) powered by the OpenKIM Deep Citation framework. The word cloud indicates typical applications of the potential. The bar chart shows citations per year of this IP (bars are divided into articles that used the IP (green) and those that did not (blue)). The complete list of articles that cited this IP is provided below along with the Deep Citation determination on usage. See the Deep Citation documentation for more information. 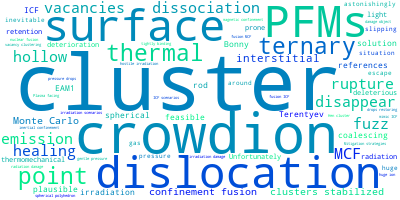
72 Citations (60 used)
Help us to determine which of the papers that cite this potential actually used it to perform calculations. If you know, click the .
USED (high confidence) J. Wang, Z. Guo, W. Dang, and D. Liu, “Molecular dynamics investigation of the configuration and shape of helium clusters in tungsten,” Nuclear Fusion. 2020. link Times cited: 4 Abstract: The stable configuration and shape of a helium cluster in tu… read more USED (high confidence) P. Díaz-Rodríguez et al., “Highly porous tungsten for plasma-facing applications in nuclear fusion power plants: a computational analysis of hollow nanoparticles,” Nuclear Fusion. 2020. link Times cited: 3 Abstract: Plasma-facing materials (PFMs) for nuclear fusion, either in… read more USED (high confidence) J. Wang, W. Dang, D. Liu, and Z. Guo, “Size effect of He clusters on the interactions with self-interstitial tungsten atoms at different temperatures,” Chinese Physics B. 2020. link Times cited: 3 Abstract: The behaviors of helium cluster and self-interstitial tungst… read more USED (high confidence) P. Grigorev et al., “Molecular dynamics simulation of hydrogen and helium trapping in tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 18 USED (high confidence) M. Qiu, L. Zhai, J. Cui, B. Fu, M. Li, and Q. Hou, “Diffusion behavior of hydrogen isotopes in tungsten revisited by molecular dynamics simulations,” Chinese Physics B. 2018. link Times cited: 8 USED (high confidence) P. Grigorev, D. Terentyev, G. Bonny, E. Zhurkin, G. Oost, and J. Noterdaeme, “Mobility of hydrogen-helium clusters in tungsten studied by molecular dynamics,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2016. link Times cited: 19 USED (high confidence) P. Grigorev, D. Terentyev, A. Bakaev, and E. E. Zhurkin, “Classical molecular dynamics simulation of the interaction of hydrogen with defects in tungsten,” Journal of Surface Investigation. X-ray, Synchrotron and Neutron Techniques. 2016. link Times cited: 4 USED (high confidence) P. Grigorev, D. Terentyev, G. Bonny, E. Zhurkin, G. Oost, and J. Noterdaeme, “Interaction of hydrogen with dislocations in tungsten: An atomistic study,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2015. link Times cited: 32 USED (high confidence) Q.-D. Meng, L. Niu, Y. Zhang, and G. Lu, “Molecular dynamics simulations of temperature effect on tungsten sputtering yields under helium bombardment,” Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy. 2017. link Times cited: 7 USED (low confidence) X.-Y. Wang et al., “Deep neural network potential for simulating hydrogen blistering in tungsten,” Physical Review Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) G. Samolyuk et al., “Crystallographic and temperature effects in low-energy collisions for plasma–material interactions,” Materialia. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) B. Xu et al., “Interaction of 1/2〈111〉 interstitial dislocation loop with hydrogen and helium in tungsten: molecular dynamics simulation,” Materials Research Express. 2023. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: The interaction of hydrogen and helium atoms with 1/2 〈111〉 … read more USED (low confidence) H. Zhang, Y.-min Wang, J.-zhong Sun, M. Qin, and T. Stirner, “Lattice thermal conductivity of defected tungsten evaluated by equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation,” Materials Today Communications. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) J. Wang et al., “Diffusion and incidence of helium on tungsten surface,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) D. Mason, D. Nguyen-Manh, V. W. Lindblad, F. Granberg, and M. Lavrentiev, “An empirical potential for simulating hydrogen isotope retention in highly irradiated tungsten,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2023. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: We describe the parameterization of a tungsten-hydrogen empi… read more USED (low confidence) H. Chen et al., “Hydrogen retention and affecting factors in rolled tungsten: Thermal desorption spectra and molecular dynamics simulations,” International Journal of Hydrogen Energy. 2023. link Times cited: 3 USED (low confidence) “The structure and energy of symmetric tilt grain boundaries in tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 1 USED (low confidence) C. Ji, J. Hu, Z. Zhuang, and Y. Cui, “Atomistically-informed hardening and kinetics models of helium bubble in irradiated tungsten,” International Journal of Plasticity. 2023. link Times cited: 2 USED (low confidence) C. Petersson, A. Fredriksson, S. Melin, A. Ahadi, and P. Hansson, “A molecular dynamics study on the influence of vacancies and interstitial helium on mechanical properties of tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) L. Yang, C. Wu, D. K. Peng, Y. J. Shen, J. Fan, and H. Gong, “Effect of Cu on strain-stress relationship of W bicrystal models with grain boundary from molecular dynamics simulation,” Vacuum. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) T. Oda, “Steady-state tritium inventory in plasma-facing tungsten for fusion reactors: an effective calculation method and implications of calculation results,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 0 USED (low confidence) T. Wang et al., “Neon-concentration dependent retarding effect on the recrystallization of irradiated tungsten: experimental analysis and molecular dynamics simulation,” Journal of Materials Science & Technology. 2022. link Times cited: 2 USED (low confidence) Y. Hu, P. Huang, and F. Wang, “Nanopore graphene-tungsten composite with enhanced irradiated helium atoms storage capacity,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2022. link Times cited: 1 USED (low confidence) R. Zheng, L. Yang, and L. Zhang, “Grain Boundary Migration as a Self-Healing Mechanism of Tungsten at High Temperature,” Metals. 2022. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: The tungsten components in nuclear fusion reactors need to w… read more USED (low confidence) J. Wang, J. Chai, W. Dang, X.-D. Pan, X. Li, and G. Luo, “Molecular dynamics study on melting point of tungsten nanostructures,” Nuclear Materials and Energy. 2022. link Times cited: 2 USED (low confidence) Y. Hu, P. Huang, and F. Wang, “Graphene distribution and structural integrity dependent irradiation resistance of graphene/tungsten composites,” Materials Today Communications. 2022. link Times cited: 4 USED (low confidence) X. Li et al., “Towards the dependence of radiation damage on the grain boundary character and grain size in tungsten: A combined study of molecular statics and rate theory,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2022. link Times cited: 8 USED (low confidence) A. Fraile, P. Dwivedi, G. Bonny, and T. Polcar, “Analysis of hypervelocity impacts: the tungsten case,” Nuclear Fusion. 2021. link Times cited: 3 Abstract: The atomistic mechanisms of damage initiation during high ve… read more USED (low confidence) O. Lindblom, T. Ahlgren, and K. Heinola, “Molecular dynamics simulations of hydrogen isotope exchange in tungsten vacancies,” Nuclear Materials and Energy. 2021. link Times cited: 3 USED (low confidence) J. Wang, D. Liu, Z. Guo, B. He, and W. Dang, “Molecular dynamics study on the origin of fuzz structure on tungsten surface,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 10 USED (low confidence) Y. Chen et al., “Energetics and diffusional properties of helium in W-Ta systems studied by a new ternary potential,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 8 USED (low confidence) J. Wang, D. Liu, W. Dang, Z. Guo, and W.-H. Song, “Segregation and coalescence behavior of helium bubbles in tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 12 USED (low confidence) A. Y. Hamid, J.-zhong Sun, H. Zhang, and T. Stirner, “Molecular dynamics simulation analysis of helium cluster growth conditions under tungsten surfaces,” Computational Materials Science. 2021. link Times cited: 3 USED (low confidence) H. Zhang, J.-zhong Sun, Y. Wang, T. Stirner, A. Y. Hamid, and C. Sang, “Study of lattice thermal conductivity of tungsten containing bubbles by molecular dynamics simulation,” Fusion Engineering and Design. 2020. link Times cited: 5 USED (low confidence) F.-F. Ma et al., “Collaborative motion of helium and self-interstitial atoms enhanced self-healing efficiency of irradiation-induced defects in tungsten,” Nuclear Fusion. 2020. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: Helium (He) is a typical impurity element and plays a crucia… read more USED (low confidence) W. Q. Chen et al., “Nucleation mechanism of intra-granular blisters in tungsten exposed to hydrogen plasma,” Scripta Materialia. 2020. link Times cited: 11 USED (low confidence) M. Ye, J. Zhan, S. Mao, Z. Liu, and Y. Ding, “Simulation study of evolution of helium induced defects in bulk tungsten,” Fusion Engineering and Design. 2020. link Times cited: 2 USED (low confidence) M. Abu-Shams, J. Moran, and I. Shabib, “Displacement cascade evolution in tungsten with pre-existing helium and hydrogen clusters: a molecular dynamics study,” International Journal of Materials Research. 2020. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: The effects of radiation damage on bcc tungsten with preexis… read more USED (low confidence) Y. Li, Q. Zheng, L. Wei, C. Zhang, and Z. Zeng, “A review of surface damage/microstructures and their effects on hydrogen/helium retention in tungsten,” Tungsten. 2020. link Times cited: 27 USED (low confidence) J. Zhan, M. Ye, S. Mao, J. Ren, and X. Xu, “Simulation study of evolution of helium bubbles in bulk tungsten,” Fusion Engineering and Design. 2019. link Times cited: 7 USED (low confidence) B. Fu, M. Qiu, J. Cui, M. Li, J. Wang, and Q. Hou, “Trapping and detrapping process of hydrogen in tungsten divacancy: A molecular dynamics study,” Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. 2019. link Times cited: 1 USED (low confidence) B. Fu, M. Qiu, L. Zhai, A. Yang, and Q. Hou, “Molecular dynamics studies of low-energy atomic hydrogen cumulative bombardment on tungsten surface,” Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms. 2019. link Times cited: 9 USED (low confidence) A. Y. Hamid, J.-zhong Sun, H. Zhang, A. S. Jadon, and T. Stirner, “Molecular dynamics simulations of helium clustering and bubble growth under tungsten surfaces,” Computational Materials Science. 2019. link Times cited: 12 USED (low confidence) L. Yang, Z. Bergstrom, and B. Wirth, “Effect of interatomic potential on the energetics of hydrogen and helium-vacancy complexes in bulk, or near surfaces of tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 17 USED (low confidence) W. Chen et al., “Characterization of dose dependent mechanical properties in helium implanted tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 23 USED (low confidence) B. Fu, M. Qiu, J. Cui, M. Li, and Q. Hou, “The trapping and dissociation process of hydrogen in tungsten vacancy: A molecular dynamics study,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 13 USED (low confidence) J. Hou et al., “Predictive model of hydrogen trapping and bubbling in nanovoids in bcc metals,” Nature Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 75 USED (low confidence) Y. Zhou, X. Tao, Q. Hou, and Y. Ouyang, “Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Atoms Diffusion in Solid,” Diffusion Foundations. 2018. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, which treat atoms as po… read more USED (low confidence) G. Bonny, N. Castin, M. I. Pascuet, Y. Çelik, and G. Cruz, “Exact mean field concept to compute defect energetics in random alloys on rigid lattices,” Physica B-condensed Matter. 2017. link Times cited: 4 USED (low confidence) A. Bakaev, D. Terentyev, P. Grigorev, M. Posselt, and E. Zhurkin, “Ab initio study of interaction of helium with edge and screw dislocations in tungsten,” Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms. 2017. link Times cited: 18 USED (low confidence) P. Grigorev, A. Bakaev, D. Terentyev, G. Oost, J. Noterdaeme, and E. Zhurkin, “Interaction of hydrogen and helium with nanometric dislocation loops in tungsten assessed by atomistic calculations,” Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms. 2017. link Times cited: 14 USED (low confidence) Z. Chen, L. Kecskes, K. Zhu, and Q. Wei, “Atomistic simulations of the effect of embedded hydrogen and helium on the tensile properties of monocrystalline and nanocrystalline tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2016. link Times cited: 30 USED (low confidence) A. Bakaeva et al., “Dislocation-mediated trapping of deuterium in tungsten under high-flux high-temperature exposures,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2016. link Times cited: 14 USED (low confidence) F. Zhou et al., “New interatomic potentials for studying the behavior of noble gas atoms in tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2015. link Times cited: 15 USED (low confidence) P. Piaggi et al., “Hydrogen diffusion and trapping in nanocrystalline tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2015. link Times cited: 43 USED (low confidence) Q.-Y. Ren et al., “Revealing the synergistic effect of invisible helium clusters in helium irradiation hardening in tungsten,” Scripta Materialia. 2022. link Times cited: 4 USED (low confidence) B. Fu, M. Qiu, J. Cui, J. Wang, and Q. Hou, “Diffusion, Trapping, and Dissociation Behaviours of Helium at the Σ5 Grain Boundary in Tungsten: A Molecular Dynamics Study,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 9 USED (low confidence) M. Qiu, A. Yang, L. Zhai, B. Fu, and Q. Hou, “The calculation of the dissociation of hydrogen from helium clusters in tungsten,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 4 USED (low confidence) B. Fu, J. Wang, M. Qiu, and H. Wang, “Retention/reflection of hydrogen and surface evolution during cumulative bombardment of low-energy hydrogen on tungsten: A molecular dynamics study,” Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-beam Interactions With Materials and Atoms. 2020. link Times cited: 6 USED (low confidence) Y. G. Osetsky and D. Rodney, “Atomic-Level Dislocation Dynamics in Irradiated Metals,” Comprehensive Nuclear Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 8 NOT USED (low confidence) С. Волегов, Р. М. Герасимов, and Р. П. Давлятшин, “MODELS OF MOLECULAR DYNAMICS: A REVIEW OF EAM-POTENTIALS. PART 2. POTENTIALS FOR MULTI-COMPONENT SYSTEMS.” 2018. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: Получена: 18 мая 2018 г. Принята: 25 июня 2018 г. Опубликова… read more NOT USED (high confidence) L. Reali, M. Gilbert, M. Boleininger, and S. Dudarev, “Intense
γ
-Photon and High-Energy Electron Production by Neutron Irradiation: Effects of Nuclear Excitations on Reactor Materials,” PRX Energy. 2022. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: The effects of neutron irradiation on materials are often in… read more NOT USED (high confidence) N. Mathew, D. Perez, and E. Martínez, “Atomistic simulations of helium, hydrogen, and self-interstitial diffusion inside dislocation cores in tungsten,” Nuclear Fusion. 2020. link Times cited: 7 Abstract: Tritium retention and microstructural modifications due to h… read more NOT USED (high confidence) D. Mason, D. Nguyen-Manh, M. Marinica, R. Alexander, A. Sand, and S. Dudarev, “Relaxation volumes of microscopic and mesoscopic irradiation-induced defects in tungsten,” Journal of Applied Physics. 2018. link Times cited: 32 Abstract: The low-energy structures of irradiation-induced defects in … read more NOT USED (high confidence) D. Mason, D. Nguyen-Manh, and C. Becquart, “An empirical potential for simulating vacancy clusters in tungsten,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2017. link Times cited: 50 Abstract: We present an empirical interatomic potential for tungsten, … read more NOT USED (high confidence) A. D. Backer et al., “Hydrogen accumulation around dislocation loops and edge dislocations: from atomistic to mesoscopic scales in BCC tungsten,” Physica Scripta. 2017. link Times cited: 13 Abstract: In a fusion tokamak, the plasma interacts with the metallic … read more NOT USED (high confidence) A. Bakaev, P. Grigorev, D. Terentyev, A. Bakaeva, E. Zhurkin, and Y. Mastrikov, “Trapping of hydrogen and helium at dislocations in tungsten: an ab initio study,” Nuclear Fusion. 2017. link Times cited: 36 Abstract: The interaction of H or He atoms with a core of edge and scr… read more NOT USED (high confidence) L.-F. Wang, X. Shu, G. Lu, and F. Gao, “Embedded-atom method potential for modeling hydrogen and hydrogen-defect interaction in tungsten,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2017. link Times cited: 20 Abstract: An embedded-atom method potential has been developed for mod… read more NOT USED (high confidence) L. Vlček, W. Sun, and P. Kent, “Combining configurational energies and forces for molecular force field optimization.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2017. link Times cited: 11 Abstract: While quantum chemical simulations have been increasingly us… read more NOT USED (high confidence) S. Markelj, T. Schwarz-Selinger, and A. Založnik, “Hydrogen isotope accumulation in the helium implantation zone in tungsten,” Nuclear Fusion. 2017. link Times cited: 34 Abstract: The influence of helium (He) on deuterium (D) transport and … read more |
| Funding | Not available |
| Short KIM ID
The unique KIM identifier code.
| MO_292520929154_000 |
| Extended KIM ID
The long form of the KIM ID including a human readable prefix (100 characters max), two underscores, and the Short KIM ID. Extended KIM IDs can only contain alpha-numeric characters (letters and digits) and underscores and must begin with a letter.
| EAM_Dynamo_BonnyGrigorevTerentyev_2014EAM1_WHHe__MO_292520929154_000 |
| DOI |
10.25950/b33a4dc7 https://doi.org/10.25950/b33a4dc7 https://commons.datacite.org/doi.org/10.25950/b33a4dc7 |
| KIM Item Type
Specifies whether this is a Portable Model (software implementation of an interatomic model); Portable Model with parameter file (parameter file to be read in by a Model Driver); Model Driver (software implementation of an interatomic model that reads in parameters).
| Portable Model using Model Driver EAM_Dynamo__MD_120291908751_005 |
| Driver | EAM_Dynamo__MD_120291908751_005 |
| KIM API Version | 2.0 |
| Potential Type | eam |
| Grade | Name | Category | Brief Description | Full Results | Aux File(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | vc-species-supported-as-stated | mandatory | The model supports all species it claims to support; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-periodicity-support | mandatory | Periodic boundary conditions are handled correctly; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-permutation-symmetry | mandatory | Total energy and forces are unchanged when swapping atoms of the same species; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| A | vc-forces-numerical-derivative | consistency | Forces computed by the model agree with numerical derivatives of the energy; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-dimer-continuity-c1 | informational | The energy versus separation relation of a pair of atoms is C1 continuous (i.e. the function and its first derivative are continuous); see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-objectivity | informational | Total energy is unchanged and forces transform correctly under rigid-body translation and rotation; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-inversion-symmetry | informational | Total energy is unchanged and forces change sign when inverting a configuration through the origin; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-memory-leak | informational | The model code does not have memory leaks (i.e. it releases all allocated memory at the end); see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-thread-safe | mandatory | The model returns the same energy and forces when computed in serial and when using parallel threads for a set of configurations. Note that this is not a guarantee of thread safety; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-unit-conversion | mandatory | The model is able to correctly convert its energy and/or forces to different unit sets; see full description. |
Results | Files |
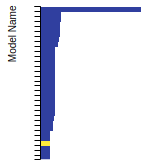
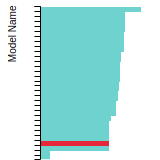
BCC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic body-centered cubic (bcc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
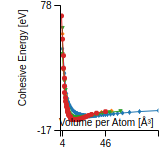
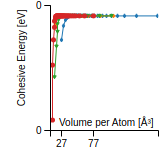
Cohesive Energy Graph
This graph shows the cohesive energy versus volume-per-atom for the current mode for four mono-atomic cubic phases (body-centered cubic (bcc), face-centered cubic (fcc), simple cubic (sc), and diamond). The curve with the lowest minimum is the ground state of the crystal if stable. (The crystal structure is enforced in these calculations, so the phase may not be stable.) Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
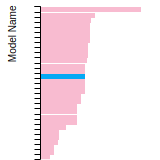
Diamond Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered diamond lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
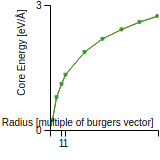
Dislocation Core Energies
This graph shows the dislocation core energy of a cubic crystal at zero temperature and pressure for a specific set of dislocation core cutoff radii. After obtaining the total energy of the system from conjugate gradient minimizations, non-singular, isotropic and anisotropic elasticity are applied to obtain the dislocation core energy for each of these supercells with different dipole distances. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
FCC Elastic Constants
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) elastic constants predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
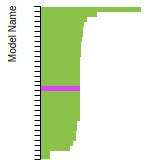
FCC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in red) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
FCC Stacking Fault Energies
This bar chart plot shows the intrinsic and extrinsic stacking fault energies as well as the unstable stacking and unstable twinning energies for face-centered cubic (fcc) predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
(No matching species)FCC Surface Energies
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) relaxed surface energies predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
(No matching species)SC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic simple cubic (sc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
Cubic Crystal Basic Properties Table
Species: HSpecies: He
Species: W
Creators: Daniel S. Karls
Contributor: karls
Publication Year: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/c6746c52
This Test Driver uses LAMMPS to compute the cohesive energy of a given monoatomic cubic lattice (fcc, bcc, sc, or diamond) at a variety of lattice spacings. The lattice spacings range from a_min (=a_min_frac*a_0) to a_max (=a_max_frac*a_0) where a_0, a_min_frac, and a_max_frac are read from stdin (a_0 is typically approximately equal to the equilibrium lattice constant). The precise scaling and number of lattice spacings sampled between a_min and a_0 (a_0 and a_max) is specified by two additional parameters passed from stdin: N_lower and samplespacing_lower (N_upper and samplespacing_upper). Please see README.txt for further details.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for bcc Helium | view | 3372 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for diamond Helium | view | 3409 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for fcc Helium | view | 3665 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for sc Helium | view | 3849 |
Creators:
Contributor: karls
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/64cb38c5
This Test Driver uses LAMMPS to compute the cohesive energy of a given monoatomic cubic lattice (fcc, bcc, sc, or diamond) at a variety of lattice spacings. The lattice spacings range from a_min (=a_min_frac*a_0) to a_max (=a_max_frac*a_0) where a_0, a_min_frac, and a_max_frac are read from stdin (a_0 is typically approximately equal to the equilibrium lattice constant). The precise scaling and number of lattice spacings sampled between a_min and a_0 (a_0 and a_max) is specified by two additional parameters passed from stdin: N_lower and samplespacing_lower (N_upper and samplespacing_upper). Please see README.txt for further details.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for bcc W v004 | view | 8544 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for diamond W v004 | view | 9120 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for fcc W v004 | view | 8822 | |
| Cohesive energy versus lattice constant curve for sc W v004 | view | 10528 |
Creators:
Contributor: qyc081025
Publication Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/ebecf626
This Test Driver computes the dislocation core energy of a cubic crystal at zero temperature and pressure for a specific set of dislocation core cutoff radii. First, it generates several periodic atomistic supercells containing a dislocation dipole. After obtaining the total energy of the system from conjugate gradient minimizations, non-singular, isotropic and anisotropic elasticity are applied to obtain the dislocation core energy for each of these supercells with different dipole distances. The supercell is increased in size until the disolcation core energy converges. Finally, after checking the independence of the results from the simulation cell geometry, the dislocation core energies are determined for each dislocation core radius.
Creators: Junhao Li
Contributor: jl2922
Publication Year: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/75393d88
Computes the cubic elastic constants for some common crystal types (fcc, bcc, sc) by calculating the hessian of the energy density with respect to strain. An estimate of the error associated with the numerical differentiation performed is reported.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic constants for bcc H at zero temperature | view | 2896 | |
| Elastic constants for bcc He at zero temperature | view | 3299 | |
| Elastic constants for fcc H at zero temperature | view | 3372 | |
| Elastic constants for fcc He at zero temperature | view | 3299 | |
| Elastic constants for sc H at zero temperature | view | 3372 | |
| Elastic constants for sc He at zero temperature | view | 2932 |
Creators: Junhao Li and Ellad Tadmor
Contributor: tadmor
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/5853fb8f
Computes the cubic elastic constants for some common crystal types (fcc, bcc, sc, diamond) by calculating the hessian of the energy density with respect to strain. An estimate of the error associated with the numerical differentiation performed is reported.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic constants for bcc W at zero temperature v006 | view | 5982 | |
| Elastic constants for diamond W at zero temperature v001 | view | 7421 | |
| Elastic constants for fcc W at zero temperature v006 | view | 1823 | |
| Elastic constants for sc W at zero temperature v006 | view | 1791 |
Creators: Junhao Li
Contributor: jl2922
Publication Year: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/2e4b93d9
Computes the elastic constants for hcp crystals by calculating the hessian of the energy density with respect to strain. An estimate of the error associated with the numerical differentiation performed is reported.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic constants for hcp H at zero temperature | view | 3335 |
Creators: Junhao Li
Contributor: jl2922
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/d794c746
Computes the elastic constants for hcp crystals by calculating the hessian of the energy density with respect to strain. An estimate of the error associated with the numerical differentiation performed is reported.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic constants for hcp W at zero temperature v004 | view | 1528 |
Creators:
Contributor: ilia
Publication Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/2f2c4ad3
Computes the equilibrium crystal structure and energy for an arbitrary crystal at zero temperature and applied stress by performing symmetry-constrained relaxation. The crystal structure is specified using the AFLOW prototype designation. Multiple sets of free parameters corresponding to the crystal prototype may be specified as initial guesses for structure optimization. No guarantee is made regarding the stability of computed equilibria, nor that any are the ground state.
Creators:
Contributor: ilia
Publication Year: 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/866c7cfa
Computes the equilibrium crystal structure and energy for an arbitrary crystal at zero temperature and applied stress by performing symmetry-constrained relaxation. The crystal structure is specified using the AFLOW prototype designation. Multiple sets of free parameters corresponding to the crystal prototype may be specified as initial guesses for structure optimization. No guarantee is made regarding the stability of computed equilibria, nor that any are the ground state.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium crystal structure and energy for W in AFLOW crystal prototype A_cF4_225_a v003 | view | 194410 | |
| Equilibrium crystal structure and energy for W in AFLOW crystal prototype A_cI2_229_a v003 | view | 138715 | |
| Equilibrium crystal structure and energy for W in AFLOW crystal prototype A_cP8_223_ac v003 | view | 234365 |
Creators: Junhao Li
Contributor: jl2922
Publication Year: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/f3eec5a9
Equilibrium lattice constant and cohesive energy of a cubic lattice at zero temperature and pressure.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for bcc H | view | 1320 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for bcc He | view | 16714 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for diamond H | view | 1539 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for diamond He | view | 77448 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for fcc H | view | 1393 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for fcc He | view | 35077 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for sc H | view | 1576 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for sc He | view | 4985 |
Creators: Daniel S. Karls and Junhao Li
Contributor: karls
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/2765e3bf
Equilibrium lattice constant and cohesive energy of a cubic lattice at zero temperature and pressure.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for bcc W v007 | view | 2175 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for diamond W v007 | view | 3519 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for fcc W v007 | view | 2495 | |
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for sc W v007 | view | 2015 |
Creators: Junhao Li
Contributor: jl2922
Publication Year: 2018
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/25bcc28b
Calculates lattice constant of hexagonal bulk structures at zero temperature and pressure by using simplex minimization to minimize the potential energy.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp H | view | 11289 |
Creators: Daniel S. Karls and Junhao Li
Contributor: karls
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/c339ca32
Calculates lattice constant of hexagonal bulk structures at zero temperature and pressure by using simplex minimization to minimize the potential energy.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp W v005 | view | 17382 |
Creators:
Contributor: mjwen
Publication Year: 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/9d9822ec
This Test Driver uses LAMMPS to compute the linear thermal expansion coefficient at a finite temperature under a given pressure for a cubic lattice (fcc, bcc, sc, diamond) of a single given species.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear thermal expansion coefficient of bcc W at 293.15 K under a pressure of 0 MPa v002 | view | 527344 |
Creators: Matt Bierbaum
Contributor: mattbierbaum
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/6c43a4e6
Calculates the surface energy of several high symmetry surfaces and produces a broken-bond model fit. In latex form, the fit equations are given by:
E_{FCC} (\vec{n}) = p_1 (4 \left( |x+y| + |x-y| + |x+z| + |x-z| + |z+y| +|z-y|\right)) + p_2 (8 \left( |x| + |y| + |z|\right)) + p_3 (2 ( |x+ 2y + z| + |x+2y-z| + |x-2y + z| + |x-2y-z| + |2x+y+z| + |2x+y-z| +|2x-y+z| +|2x-y-z| +|x+y+2z| +|x+y-2z| +|x-y+2z| +|x-y-2z| ) + c
E_{BCC} (\vec{n}) = p_1 (6 \left( | x+y+z| + |x+y-z| + |-x+y-z| + |x-y+z| \right)) + p_2 (8 \left( |x| + |y| + |z|\right)) + p_3 (4 \left( |x+y| + |x-y| + |x+z| + |x-z| + |z+y| +|z-y|\right)) +c.
In Python, these two fits take the following form:
def BrokenBondFCC(params, index):
import numpy
x, y, z = index
x = x / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
y = y / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
z = z / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
return params[0]*4* (abs(x+y) + abs(x-y) + abs(x+z) + abs(x-z) + abs(z+y) + abs(z-y)) + params[1]*8*(abs(x) + abs(y) + abs(z)) + params[2]*(abs(x+2*y+z) + abs(x+2*y-z) +abs(x-2*y+z) +abs(x-2*y-z) + abs(2*x+y+z) +abs(2*x+y-z) +abs(2*x-y+z) +abs(2*x-y-z) + abs(x+y+2*z) +abs(x+y-2*z) +abs(x-y+2*z) +abs(x-y-2*z))+params[3]
def BrokenBondBCC(params, x, y, z):
import numpy
x, y, z = index
x = x / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
y = y / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
z = z / numpy.sqrt(x**2.+y**2.+z**2.)
return params[0]*6*(abs(x+y+z) + abs(x-y-z) + abs(x-y+z) + abs(x+y-z)) + params[1]*8*(abs(x) + abs(y) + abs(z)) + params[2]*4* (abs(x+y) + abs(x-y) + abs(x+z) + abs(x-z) + abs(z+y) + abs(z-y)) + params[3]
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Broken-bond fit of high-symmetry surface energies in bcc W v004 | view | 15963 |
Creators:
Contributor: efuem
Publication Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/fca89cea
Computes the monovacancy formation energy and relaxation volume for cubic and hcp monoatomic crystals.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monovacancy formation energy and relaxation volume for bcc W | view | 239561 |
Creators:
Contributor: efuem
Publication Year: 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/c27ba3cd
Computes the monovacancy formation and migration energies for cubic and hcp monoatomic crystals.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacancy formation and migration energy for bcc W | view | 4638312 |
LatticeConstantCubicEnergy__TD_475411767977_007
LatticeConstantHexagonalEnergy__TD_942334626465_005
| Test | Error Categories | Link to Error page |
|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp H v005 | other | view |
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp He v005 | other | view |
| EAM_Dynamo_BonnyGrigorevTerentyev_2014EAM1_WHHe__MO_292520929154_000.txz | Tar+XZ | Linux and OS X archive |
| EAM_Dynamo_BonnyGrigorevTerentyev_2014EAM1_WHHe__MO_292520929154_000.zip | Zip | Windows archive |
This Model requires a Model Driver. Archives for the Model Driver EAM_Dynamo__MD_120291908751_005 appear below.
| EAM_Dynamo__MD_120291908751_005.txz | Tar+XZ | Linux and OS X archive |
| EAM_Dynamo__MD_120291908751_005.zip | Zip | Windows archive |