Citations
This panel presents information regarding the papers that have cited the interatomic potential (IP) whose page you are on.
The OpenKIM machine learning based Deep Citation framework is used to determine whether the citing article actually used the IP in computations (denoted by "USED") or only provides it as a background citation (denoted by "NOT USED"). For more details on Deep Citation and how to work with this panel, click the documentation link at the top of the panel.
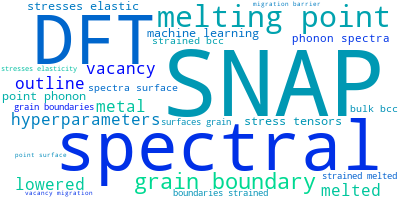
The word cloud to the right is generated from the abstracts of IP principle source(s) (given below in "How to Cite") and the citing articles that were determined to have used the IP in order to provide users with a quick sense of the types of physical phenomena to which this IP is applied.
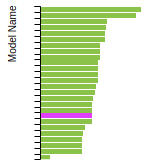
The bar chart shows the number of articles that cited the IP per year. Each bar is divided into green (articles that USED the IP) and blue (articles that did NOT USE the IP).
Users are encouraged to correct Deep Citation errors in determination by clicking the speech icon next to a citing article and providing updated information. This will be integrated into the next Deep Citation learning cycle, which occurs on a regular basis.
OpenKIM acknowledges the support of the Allen Institute for AI through the Semantic Scholar project for providing citation information and full text of articles when available, which are used to train the Deep Citation ML algorithm.
|
This panel provides information on past usage of this interatomic potential (IP) powered by the OpenKIM Deep Citation framework. The word cloud indicates typical applications of the potential. The bar chart shows citations per year of this IP (bars are divided into articles that used the IP (green) and those that did not (blue)). The complete list of articles that cited this IP is provided below along with the Deep Citation determination on usage. See the Deep Citation documentation for more information.
85 Citations (5 used)
Help us to determine which of the papers that cite this potential actually used it to perform calculations. If you know, click the .
USED (high confidence) B. Waters, D. S. Karls, I. Nikiforov, R. Elliott, E. Tadmor, and B. Runnels, “Automated determination of grain boundary energy and potential-dependence using the OpenKIM framework,” Computational Materials Science. 2022. link Times cited: 5 USED (low confidence) T. Miyagawa, Y. Sakai, K. Mori, N. Kato, A. Yonezu, and K. Ishibashi, “Distribution of the Mechanical Properties of Ti–Cu Combinatorial Thin Film Evaluated Using Nanoindentation Experiments and Molecular Dynamics with a Neural Network Potential,” SSRN Electronic Journal. 2022. link Times cited: 1 USED (low confidence) A. Shrestha, X. Gao, J. Hicks, and C. Paolucci, “Nanoparticle Size Effects on Phase Stability for Molybdenum and Tungsten Carbides,” Chemistry of Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 15 USED (low confidence) S. Fujii and A. Seko, “Structure and lattice thermal conductivity of grain boundaries in silicon by using machine learning potential and molecular dynamics,” Computational Materials Science. 2021. link Times cited: 8 USED (low confidence) X. Gu and C. Y. Zhao, “Thermal conductivity of single-layer MoS2(1−x)Se2x alloys from molecular dynamics simulations with a machine-learning-based interatomic potential,” Computational Materials Science. 2019. link Times cited: 47 NOT USED (low confidence) X. Qian, B.-J. Yoon, R. Arróyave, X. Qian, and E. R. Dougherty, “Knowledge-driven learning, optimization, and experimental design under uncertainty for materials discovery,” Patterns. 2023. link Times cited: 0 NOT USED (low confidence) R. Feng et al., “PolyGET: Accelerating Polymer Simulations by Accurate and Generalizable Forcefield with Equivariant Transformer,” ArXiv. 2023. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: Polymer simulation with both accuracy and efficiency is a ch… read moreAbstract: Polymer simulation with both accuracy and efficiency is a challenging task. Machine learning (ML) forcefields have been developed to achieve both the accuracy of ab initio methods and the efficiency of empirical force fields. However, existing ML force fields are usually limited to single-molecule settings, and their simulations are not robust enough. In this paper, we present PolyGET, a new framework for Polymer Forcefields with Generalizable Equivariant Transformers. PolyGET is designed to capture complex quantum interactions between atoms and generalize across various polymer families, using a deep learning model called Equivariant Transformers. We propose a new training paradigm that focuses exclusively on optimizing forces, which is different from existing methods that jointly optimize forces and energy. This simple force-centric objective function avoids competing objectives between energy and forces, thereby allowing for learning a unified forcefield ML model over different polymer families. We evaluated PolyGET on a large-scale dataset of 24 distinct polymer types and demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in force accuracy and robust MD simulations. Furthermore, PolyGET can simulate large polymers with high fidelity to the reference ab initio DFT method while being able to generalize to unseen polymers. read less NOT USED (low confidence) J. P. Stoppelman, A. Wilkinson, and J. G. McDaniel, “Equation of state predictions for ScF3 and CaZrF6 with neural network-driven molecular dynamics.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2023. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: In silico property prediction based on density functional th… read moreAbstract: In silico property prediction based on density functional theory (DFT) is increasingly performed for crystalline materials. Whether quantitative agreement with experiment can be achieved with current methods is often an unresolved question, and may require detailed examination of physical effects such as electron correlation, reciprocal space sampling, phonon anharmonicity, and nuclear quantum effects (NQE), among others. In this work, we attempt first-principles equation of state prediction for the crystalline materials ScF3 and CaZrF6, which are known to exhibit negative thermal expansion (NTE) over a broad temperature range. We develop neural network (NN) potentials for both ScF3 and CaZrF6 trained to extensive DFT data, and conduct direct molecular dynamics prediction of the equation(s) of state over a broad temperature/pressure range. The NN potentials serve as surrogates of the DFT Hamiltonian with enhanced computational efficiency allowing for simulations with larger supercells and inclusion of NQE utilizing path integral approaches. The conclusion of the study is mixed: while some equation of state behavior is predicted in semiquantitative agreement with experiment, the pressure-induced softening phenomenon observed for ScF3 is not captured in our simulations. We show that NQE have a moderate effect on NTE at low temperature but does not significantly contribute to equation of state predictions at increasing temperature. Overall, while the NN potentials are valuable for property prediction of these NTE (and related) materials, we infer that a higher level of electron correlation, beyond the generalized gradient approximation density functional employed here, is necessary for achieving quantitative agreement with experiment. read less NOT USED (low confidence) D. F. T. du Toit and V. L. Deringer, “Cross-platform hyperparameter optimization for machine learning interatomic potentials.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2023. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: Machine-learning (ML)-based interatomic potentials are incre… read moreAbstract: Machine-learning (ML)-based interatomic potentials are increasingly popular in material modeling, enabling highly accurate simulations with thousands and millions of atoms. However, the performance of machine-learned potentials depends strongly on the choice of hyperparameters-that is, of those parameters that are set before the model encounters data. This problem is particularly acute where hyperparameters have no intuitive physical interpretation and where the corresponding optimization space is large. Here, we describe an openly available Python package that facilitates hyperparameter optimization across different ML potential fitting frameworks. We discuss methodological aspects relating to the optimization itself and to the selection of validation data, and we show example applications. We expect this package to become part of a wider computational framework to speed up the mainstream adaptation of ML potentials in the physical sciences. read less NOT USED (low confidence) W. Du, X. Fan, H. Li, D. Zhai, and Y. Liu, “Development of a Ni-Al Reactive Force Field for Ni-Based Superalloy: Revealing Electrostatic Effects on Mechanical Deformation,” SSRN Electronic Journal. 2023. link Times cited: 0 NOT USED (low confidence) R. Guo, G. Li, J. Tang, Y. Wang, and X. Song, “Small-data-based Machine Learning Interatomic Potentials for Graphene Grain Boundaries Enabled by Structural Unit Model,” Carbon Trends. 2023. link Times cited: 2 NOT USED (low confidence) J. Jiang, L.-C. Xu, F. Li, and J. Shao, “Machine Learning Potential Model Based on Ensemble Bispectrum Feature Selection and Its Applicability Analysis,” Metals. 2023. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: With the continuous improvement of machine learning methods,… read moreAbstract: With the continuous improvement of machine learning methods, building the interatomic machine learning potential (MLP) based on the datasets from quantum mechanics calculations has become an effective technical approach to improving the accuracy of classical molecular dynamics simulation. The Spectral Neighbor Analysis Potential (SNAP) is one of the most commonly used machine learning potentials. It uses the bispectrum to encode the local environment of each atom in the lattice. The hyperparameter jmax controls the mapping complexity and precision between the local environment and the bispectrum descriptor. As the hyperparameter jmax increases, the description will become more accurate, but the number of parameters in the bispectrum descriptor will increase dramatically, increasing the computational complexity. In order to reduce the computational complexity without losing the computational accuracy, this paper proposes a two-level ensemble feature selection method (EFS) for a bispectrum descriptor, combining the perturbation method and the feature selector ensemble strategy. Based on the proposed method, the feature subset is selected from the original dataset of the bispectrum descriptor for building the dimension-reduced MLP. As a method application and validation, the data of Fe, Ni, Cu, Li, Mo, Si, and Ge metal elements are used to train the linear regression model based on SNAP for predicting these metals’ atomic energies and forces them to evaluate the performance of the feature subsets. The experimental results show that, compared to the features of SNAP and qSNAP, the training complexity improvement of our EFS method on the qSNAP feature is more effective than SNAP. Compared with the existing methods, when the feature subset size is 0.7 times that of the original features, the proposed EFS method based on the SSWRP ensemble strategy can achieve the best performance in terms of stability, achieving an average stability of 0.94 across all datasets. The training complexity of the linear regression model is reduced by about half, and the prediction complexity is reduced by about 30%. read less NOT USED (low confidence) S. Blücher, K.-R. Müller, and S. Chmiela, “Reconstructing Kernel-Based Machine Learning Force Fields with Superlinear Convergence,” Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 2022. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: Kernel machines have sustained continuous progress in the fi… read moreAbstract: Kernel machines have sustained continuous progress in the field of quantum chemistry. In particular, they have proven to be successful in the low-data regime of force field reconstruction. This is because many equivariances and invariances due to physical symmetries can be incorporated into the kernel function to compensate for much larger data sets. So far, the scalability of kernel machines has however been hindered by its quadratic memory and cubical runtime complexity in the number of training points. While it is known that iterative Krylov subspace solvers can overcome these burdens, their convergence crucially relies on effective preconditioners, which are elusive in practice. Effective preconditioners need to partially presolve the learning problem in a computationally cheap and numerically robust manner. Here, we consider the broad class of Nyström-type methods to construct preconditioners based on successively more sophisticated low-rank approximations of the original kernel matrix, each of which provides a different set of computational trade-offs. All considered methods aim to identify a representative subset of inducing (kernel) columns to approximate the dominant kernel spectrum. read less NOT USED (low confidence) H. Deng, J. Comer, and B. Liu, “A high-dimensional neural network potential for molecular dynamics simulations of condensed phase nickel and phase transitions,” Molecular Simulation. 2022. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: ABSTRACT A high-dimensional neural network interatomic poten… read moreAbstract: ABSTRACT A high-dimensional neural network interatomic potential was developed and used in molecular dynamics simulations of condensed phase Ni and Ni systems with liquid–solid phase coexistence. The reference data set was generated by sampling the potential energy surface over a broad temperature-pressure domain using ab initio MD simulations to train a unified potential. Excellent agreement was achieved between bulk face-centred cubic nickel thermal expansion simulations and relevant experimental data. The same potential also yields accurate structures and diffusivities in the liquid state. The phase transition between liquid and solid phases was simulated using the two-phase interface method. The predicted melting point temperature is within a few kelvins of the literature value. The general methodology could be applied to describe crystals with much more complex phase behaviours. read less NOT USED (low confidence) K. Pitike and W. Setyawan, “Accurate Fe–He machine learning potential for studying He effects in BCC-Fe,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2022. link Times cited: 1 NOT USED (low confidence) B. Bishnoi, “Lagrangian Density Space-Time Deep Neural Network Topology,” ArXiv. 2022. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: As a network-based functional approximator, we have proposed… read moreAbstract: As a network-based functional approximator, we have proposed a"Lagrangian Density Space-Time Deep Neural Networks"(LDDNN) topology. It is qualified for unsupervised training and learning to predict the dynamics of underlying physical science governed phenomena. The prototypical network respects the fundamental conservation laws of nature through the succinctly described Lagrangian and Hamiltonian density of the system by a given data-set of generalized nonlinear partial differential equations. The objective is to parameterize the Lagrangian density over a neural network and directly learn from it through data instead of hand-crafting an exact time-dependent"Action solution"of Lagrangian density for the physical system. With this novel approach, can understand and open up the information inference aspect of the"Black-box deep machine learning representation"for the physical dynamics of nature by constructing custom-tailored network interconnect topologies, activation, and loss/cost functions based on the underlying physical differential operators. This article will discuss statistical physics interpretation of neural networks in the Lagrangian and Hamiltonian domains. read less NOT USED (low confidence) T. Miyagawa, K. Mori, N. Kato, and A. Yonezu, “Development of neural network potential for MD simulation and its application to TiN,” Computational Materials Science. 2022. link Times cited: 3 NOT USED (low confidence) T. Wen, L. Zhang, H. Wang, W. E, and D. Srolovitz, “Deep Potentials for Materials Science,” Materials Futures. 2022. link Times cited: 54 Abstract:
To fill the gap between accurate (and expensive) ab initio… read moreAbstract:
To fill the gap between accurate (and expensive) ab initio calculations and efficient atomistic simulations based on empirical interatomic potentials, a new class of descriptions of atomic interactions has emerged and been widely applied; i.e., machine learning potentials (MLPs). One recently developed type of MLP is the Deep Potential (DP) method. In this review, we provide an introduction to DP methods in computational materials science. The theory underlying the DP method is presented along with a step-by-step introduction to their development and use. We also review materials applications of DPs in a wide range of materials systems. The DP Library provides a platform for the development of DPs and a database of extant DPs. We discuss the accuracy and efficiency of DPs compared with ab initio methods and empirical potentials. read less NOT USED (low confidence) K. Xie et al., “Neural network potential for Zr–Rh system by machine learning,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2021. link Times cited: 3 Abstract: Zr–Rh metallic glass has enabled its many applications in ve… read moreAbstract: Zr–Rh metallic glass has enabled its many applications in vehicle parts, sports equipment and so on due to its outstanding performance in mechanical property, but the knowledge of the microstructure determining the superb mechanical property remains yet insufficient. Here, we develop a deep neural network potential of Zr–Rh system by using machine learning, which breaks the dilemma between the accuracy and efficiency in molecular dynamics simulations, and greatly improves the simulation scale in both space and time. The results show that the structural features obtained from the neural network method are in good agreement with the cases in ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. Furthermore, we build a large model of 5400 atoms to explore the influences of simulated size and cooling rate on the melt-quenching process of Zr77Rh23. Our study lays a foundation for exploring the complex structures in amorphous Zr77Rh23, which is of great significance for the design and practical application. read less NOT USED (low confidence) X. Chen et al., “Machine learning enhanced empirical potentials for metals and alloys,” Comput. Phys. Commun. 2021. link Times cited: 5 NOT USED (low confidence) M. Gilbert et al., “Perspectives on multiscale modelling and experiments to accelerate materials development for fusion,” Journal of Nuclear Materials. 2021. link Times cited: 33 NOT USED (low confidence) X. Wang, S. Xu, W. Jian, X.-G. Li, Y. Su, and I. Beyerlein, “Generalized stacking fault energies and Peierls stresses in refractory body-centered cubic metals from machine learning-based interatomic potentials,” Computational Materials Science. 2021. link Times cited: 30 NOT USED (low confidence) R. V. Babu, G.Ayyappan, and A.Kumaravel, “EXPLORATORY DATA ANALYSIS ON MACROSCOPIC MATERIAL BEHAVIOR USING MICROMECHANICAL SIMULATIONS BY APPLYING THE GAUSSIAN PROCESSES WITH VARIOUS KERNELS,” Indian Journal of Computer Science and Engineering. 2021. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: Pro Vice Chancellor, Galgotias University, Greater Noida, Ut… read moreAbstract: Pro Vice Chancellor, Galgotias University, Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India.1 Associate Professor, Department of Information Technology, Prince Shri Venkateshwara Padmavathy Engineering College, Chennai.2 Professor, Dean School of Computing, Bharath Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai. 3 rvbaboo76@gmail.com1 , ayyappangmca@gmail.com2, drkumaravel@gmail.com 3 Abstract New materials can bring about tremendous progress in technology and applications. However, the commonly used trial-and-error method cannot meet the current need for new materials. Now, a newly proposed idea of using deductive learning to explore new materials is becoming popular. Deductive learning finds the hidden information in a database. This research work emphases on the capturing the macroscopic material behavior and their relations with the micromechanical simulations are trains the Deductive Learning algorithms. The quality of the Deductive Learning algorithms are only as good as that of the micromechanical model and it is need to validate the new model. It is proposing a novel deductive learning approaches to model macroscopic material behavior using micromechanical simulations to capture the mechanical reply of a variety of microstructures under dissimilar loads. read less NOT USED (low confidence) H. Yanxon, D. Zagaceta, B. Tang, D. Matteson, and Q. Zhu, “PyXtal_FF: a python library for automated force field generation,” Machine Learning: Science and Technology. 2020. link Times cited: 15 Abstract: We present PyXtal_FF—a package based on Python programming l… read moreAbstract: We present PyXtal_FF—a package based on Python programming language—for developing machine learning potentials (MLPs). The aim of PyXtal_FF is to promote the application of atomistic simulations through providing several choices of atom-centered descriptors and machine learning regressions in one platform. Based on the given choice of descriptors (including the atom-centered symmetry functions, embedded atom density, SO4 bispectrum, and smooth SO3 power spectrum), PyXtal_FF can train MLPs with either generalized linear regression or neural network models, by simultaneously minimizing the errors of energy/forces/stress tensors in comparison with the data from ab-initio simulations. The trained MLP model from PyXtal_FF is interfaced with the Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE) package, which allows different types of light-weight simulations such as geometry optimization, molecular dynamics simulation, and physical properties prediction. Finally, we will illustrate the performance of PyXtal_FF by applying it to investigate several material systems, including the bulk SiO2, high entropy alloy NbMoTaW, and elemental Pt for general purposes. Full documentation of PyXtal_FF is available at https://pyxtal-ff.readthedocs.io. read less NOT USED (low confidence) P. Pattnaik, S. Raghunathan, T. Kalluri, P. Bhimalapuram, C. V. Jawahar, and U. Priyakumar, “Machine Learning for Accurate Force Calculations in Molecular Dynamics Simulations.,” The journal of physical chemistry. A. 2020. link Times cited: 32 Abstract: The computationally expensive nature of ab initio molecular … read moreAbstract: The computationally expensive nature of ab initio molecular dynamics simulations severely limits its ability to simulate large system sizes and long time scales, both of which are necessary to imitate experimental conditions. In this work, we explore an approach to make use of the data obtained using the quantum mechanical density functional theory (DFT) on small systems and use deep learning to subsequently simulate large systems by taking liquid argon as a test case. A suitable vector representation was chosen to represent the surrounding environment of each Ar atom, and a ΔNetFF machine learning model where, the neural network was trained to predict the difference in resultant forces obtained by DFT and classical force fields was introduced. Molecular dynamics simulations were then performed using forces from the neural network for various system sizes and time scales depending on the properties we calculated. A comparison of properties obtained from the classical force field and the neural network model was presented alongside available experimental data to validate the proposed method. read less NOT USED (low confidence) X. Chen, X. Gao, Y. Zhao, D. Lin, W. Chu, and H. Song, “TensorAlloy: An automatic atomistic neural network program for alloys,” Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020. link Times cited: 10 NOT USED (low confidence) G. Pilania, P. Balachandran, J. Gubernatis, and T. Lookman, “Data-Based Methods for Materials Design and Discovery: Basic Ideas and General Methods.” 2020. link Times cited: 11 Abstract: Machine learning methods are changing the way we design and … read moreAbstract: Machine learning methods are changing the way we design and discover new materials. This book provides an overview of approaches successfully used in addressing materials problems (alloys,... read less NOT USED (low confidence) J. Chapman, R. Batra, and R. Ramprasad, “Machine learning models for the prediction of energy, forces, and stresses for Platinum,” Computational Materials Science. 2020. link Times cited: 18 NOT USED (low confidence) A. V. der Ven, Z. Deng, S. Banerjee, and S. Ong, “Rechargeable Alkali-Ion Battery Materials: Theory and Computation.,” Chemical reviews. 2020. link Times cited: 116 Abstract: Since its development in the 1970s, the rechargeable alkali-… read moreAbstract: Since its development in the 1970s, the rechargeable alkali-ion battery has proven to be a truly transformative technology, providing portable energy storage for devices ranging from small portable electronics to sizable electric vehicles. Here, we present a review of modern theoretical and computational approaches to the study and design of rechargeable alkali-ion battery materials. Starting from fundamental thermodynamics and kinetics phenomenological equations, we rigorously derive the theoretical relationships for key battery properties, such as voltage, capacity, alkali diffusivity, and other electrochemically relevant computable quantities. We then present an overview of computational techniques for the study of rechargeable alkali-ion battery materials, followed by a critical review of the literature applying these techniques to yield crucial insights into battery operation and performance. Finally, we provide perspectives on outstanding challenges and opportunities in the theory and computation of rechargeable alkali-ion battery materials. read less NOT USED (low confidence) T. J. Oweida, A.-U. Mahmood, M. D. Manning, S. Rigin, and Y. G. Yingling, “Merging Materials and Data Science: Opportunities, Challenges, and Education in Materials Informatics,” MRS Advances. 2020. link Times cited: 6 Abstract: Since the launch of the Materials Genome Initiative (MGI) th… read moreAbstract: Since the launch of the Materials Genome Initiative (MGI) the field of materials informatics (MI) emerged to remove the bottlenecks limiting the pathway towards rapid materials discovery. Although the machine learning (ML) and optimization techniques underlying MI were developed well over a decade ago, programs such as the MGI encouraged researchers to make the technical advancements that make these tools suitable for the unique challenges in materials science and engineering. Overall, MI has seen a remarkable rate in adoption over the past decade. However, for the continued growth of MI, the educational challenges associated with applying data science techniques to analyse materials science and engineering problems must be addressed. In this paper, we will discuss the growing use of materials informatics in academia and industry, highlight the need for educational advances in materials informatics, and discuss the implementation of a materials informatics course into the curriculum to jump-start interested students with the skills required to succeed in materials informatics projects. read less NOT USED (low confidence) L. Tang, Z.-J. Yang, T. Wen, K. Ho, M. Kramer, and C. Wang, “Development of interatomic potential for Al-Tb alloys using a deep neural network learning method.,” Physical chemistry chemical physics : PCCP. 2020. link Times cited: 17 Abstract: An interatomic potential for the Al-Tb alloy around the comp… read moreAbstract: An interatomic potential for the Al-Tb alloy around the composition of Al90Tb10 is developed using the deep neural network (DNN) learning method. The atomic configurations and the corresponding total potential energies and forces on each atom obtained from ab initio molecular dynamics (AIMD) simulations are collected to train a DNN model to construct the interatomic potential for the Al-Tb alloy. We show that the obtained DNN model can well reproduce the energies and forces calculated by AIMD simulations. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations using the DNN interatomic potential also accurately describe the structural properties of the Al90Tb10 liquid, such as partial pair correlation functions (PPCFs) and bond angle distributions, in comparison with the results from AIMD simulations. Furthermore, the developed DNN interatomic potential predicts the formation energies of the crystalline phases of the Al-Tb system with an accuracy comparable to ab initio calculations. The structure factors of the Al90Tb10 metallic liquid and glass obtained by MD simulations using the developed DNN interatomic potential are also in good agreement with the experimental X-ray diffraction data. The development of short-range order (SRO) in the Al90Tb10 liquid and the undercooled liquid is also analyzed and three dominant SROs, i.e., Al-centered distorted icosahedron (DISICO) and Tb-centered '3661' and '15551' clusters, respectively, are identified. read less NOT USED (low confidence) D. Smirnova et al., “Atomistic description of self-diffusion in molybdenum: A comparative theoretical study of non-Arrhenius behavior,” Physical Review Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 16 Abstract: According to experimental observations, the temperature depe… read moreAbstract: According to experimental observations, the temperature dependence of self-diffusion coefficient in most body-centered cubic metals (bcc) exhibits non-Arrhenius behavior. The origin of this behavio ... read less NOT USED (low confidence) W. Zhang, S. Byna, C. Niu, and Y. Chen, “Exploring Metadata Search Essentials for Scientific Data Management,” 2019 IEEE 26th International Conference on High Performance Computing, Data, and Analytics (HiPC). 2019. link Times cited: 10 Abstract: Scientific experiments and observations store massive amount… read moreAbstract: Scientific experiments and observations store massive amounts of data in various scientific file formats. Metadata, which describes the characteristics of the data, is commonly used to sift through massive datasets in order to locate data of interest to scientists. Several indexing data structures (such as hash tables, trie, self-balancing search trees, sparse array, etc.) have been developed as part of efforts to provide an efficient method for locating target data. However, efficient determination of an indexing data structure remains unclear in the context of scientific data management, due to the lack of investigation on metadata, metadata queries, and corresponding data structures. In this study, we perform a systematic study of the metadata search essentials in the context of scientific data management. We study a real-world astronomy observation dataset and explore the characteristics of the metadata in the dataset. We also study possible metadata queries based on the discovery of the metadata characteristics and evaluate different data structures for various types of metadata attributes. Our evaluation on real-world dataset suggests that trie is a suitable data structure when prefix/suffix query is required, otherwise hash table should be used. We conclude our study with a summary of our findings. These findings provide a guideline and offers insights in developing metadata indexing methodologies for scientific applications. read less NOT USED (low confidence) W. Zhang, S. Byna, H. Tang, B. Williams, and Y. Chen, “MIQS: metadata indexing and querying service for self-describing file formats,” Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. 2019. link Times cited: 10 Abstract: Scientific applications often store datasets in self-describ… read moreAbstract: Scientific applications often store datasets in self-describing data file formats, such as HDF5 and netCDF. Regrettably, to efficiently search the metadata within these files remains challenging due to the sheer size of the datasets. Existing solutions extract the metadata and store it in external database management systems (DBMS) to locate desired data. However, this practice introduces significant overhead and complexity in extraction and querying. In this research, we propose a novel Metadata Indexing and Querying Service (MIQS), which removes the external DBMS and utilizes in-memory index to achieve efficient metadata searching. MIQS follows the self-contained data management paradigm and provides portable and schema-free metadata indexing and querying functionalities for self-describing file formats. We have evaluated MIQS with the state-of-the-art MongoDB-based metadata indexing solution. MIQS achieved up to 99% time reduction in index construction and up to 172kx search performance improvement with up to 75% reduction in memory footprint. read less NOT USED (low confidence) T. D. Huan, R. Batra, J. Chapman, C. Kim, A. Chandrasekaran, and R. Ramprasad, “Iterative-Learning Strategy for the Development of Application-Specific Atomistic Force Fields,” The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2019. link Times cited: 18 Abstract: Emerging data-driven approaches in materials science have tr… read moreAbstract: Emerging data-driven approaches in materials science have triggered the development of numerous machine-learning force fields. In practice, they are constructed by training a statistical model on a reference database to predict potential energy and/or atomic forces. Although most of the force fields can accurately recover the properties of the training set, some of them are becoming useful for actual molecular dynamics simulations. In this work, we employ a simple iterative-learning strategy for the development of machine-learning force fields targeted at specific simulations (applications). The strategy involves (1) preparing and fingerprinting a diverse reference database of atomic configurations and forces, (2) generating a pool of machine-learning force fields by learning the reference data, (3) validating the force fields against a series of targeted applications, and (4) selectively and recursively improving the force fields that are unsuitable for a given application while keeping their performance... read less NOT USED (low confidence) A. Goryaeva, J. Maillet, and M. Marinica, “Towards better efficiency of interatomic linear machine learning potentials,” Computational Materials Science. 2019. link Times cited: 34 NOT USED (low confidence) Y. Zuo et al., “A Performance and Cost Assessment of Machine Learning Interatomic Potentials.,” The journal of physical chemistry. A. 2019. link Times cited: 413 Abstract: Machine learning of the quantitative relationship between lo… read moreAbstract: Machine learning of the quantitative relationship between local environment descriptors and the potential energy surface of a system of atoms has emerged as a new frontier in the development of interatomic potentials (IAPs). Here, we present a comprehensive evaluation of ML-IAPs based on four local environment descriptors --- atom-centered symmetry functions (ACSF), smooth overlap of atomic positions (SOAP), the Spectral Neighbor Analysis Potential (SNAP) bispectrum components, and moment tensors --- using a diverse data set generated using high-throughput density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The data set comprising bcc (Li, Mo) and fcc (Cu, Ni) metals and diamond group IV semiconductors (Si, Ge) is chosen to span a range of crystal structures and bonding. All descriptors studied show excellent performance in predicting energies and forces far surpassing that of classical IAPs, as well as predicting properties such as elastic constants and phonon dispersion curves. We observe a general trade-off between accuracy and the degrees of freedom of each model, and consequently computational cost. We will discuss these trade-offs in the context of model selection for molecular dynamics and other applications. read less NOT USED (low confidence) S. Ong, “Accelerating materials science with high-throughput computations and machine learning,” Computational Materials Science. 2019. link Times cited: 66 NOT USED (low confidence) A. Hernandez, A. Balasubramanian, F. Yuan, S. Mason, and T. Mueller, “Fast, accurate, and transferable many-body interatomic potentials by symbolic regression,” npj Computational Materials. 2019. link Times cited: 51 NOT USED (low confidence) C. Chen, W. Ye, Y. Zuo, C. Zheng, and S. Ong, “Graph Networks as a Universal Machine Learning Framework for Molecules and Crystals,” Chemistry of Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 602 Abstract: Graph networks are a new machine learning (ML) paradigm that… read moreAbstract: Graph networks are a new machine learning (ML) paradigm that supports both relational reasoning and combinatorial generalization. Here, we develop, for the first time, universal MatErials Graph Network (MEGNet) models for accurate property prediction in both molecules and crystals. We demonstrate that our MEGNet models significantly outperform prior ML models in 11 out of 13 properties of the QM9 molecule data set. Furthermore, a single-task unified MEGNet model can accurately predict the internal energy at 0 K and room temperature, enthalpy and Gibbs free energy, with temperature, pressure and entropy being global state inputs. Similarly, we show that MEGNet models trained on $\sim 60,000$ crystals in the Materials Project substantially outperform prior ML models in the prediction of the formation energies, band gaps and elastic moduli of crystals, achieving better than DFT accuracy over a much larger data set. Such MEGNet models are highly interpretable, and well-established periodic chemical trends can be extracted from the elemental embeddings. Finally, we demonstrate the transfer learning of elemental embeddings from a property model trained on a larger data set (formation energies) to accelerate the training of property models with smaller amounts of data (band gaps and elastic moduli) read less NOT USED (low confidence) W. Zhang, H. Tang, S. Byna, and Y. Chen, “DART: distributed adaptive radix tree for efficient affix-based keyword search on HPC systems,” Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques. 2018. link Times cited: 10 Abstract: Affix-based search is a fundamental functionality for storag… read moreAbstract: Affix-based search is a fundamental functionality for storage systems. It allows users to find desired datasets, where attributes of a dataset match an affix. While building inverted index to facilitate efficient affix-based keyword search is a common practice for standalone databases and for desktop file systems, building local indexes or adopting indexing techniques used in a standalone data store is insufficient for high-performance computing (HPC) systems due to the massive amount of data and distributed nature of the storage devices within a system. In this paper, we propose Distributed Adaptive Radix Tree (DART), to address the challenge of distributed affix-based keyword search on HPC systems. This trie-based approach is scalable in achieving efficient affix-based search and alleviating imbalanced keyword distribution and excessive requests on keywords at scale. Our evaluation at different scales shows that, comparing with the "full string hashing" use case of the most popular distributed indexing technique - Distributed Hash Table (DHT), DART achieves up to 55× better throughput with prefix search and with suffix search, while achieving comparable throughput with exact and infix searches. Also, comparing to the "initial hashing" use case of DHT, DART maintains a balanced keyword distribution on distributed nodes and alleviates excessive query workload against popular keywords. read less NOT USED (low confidence) M. Wood and A. Thompson, “Extending the accuracy of the SNAP interatomic potential form.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2017. link Times cited: 130 Abstract: The Spectral Neighbor Analysis Potential (SNAP) is a classic… read moreAbstract: The Spectral Neighbor Analysis Potential (SNAP) is a classical interatomic potential that expresses the energy of each atom as a linear function of selected bispectrum components of the neighbor atoms. An extension of the SNAP form is proposed that includes quadratic terms in the bispectrum components. The extension is shown to provide a large increase in accuracy relative to the linear form, while incurring only a modest increase in computational cost. The mathematical structure of the quadratic SNAP form is similar to the embedded atom method (EAM), with the SNAP bispectrum components serving as counterparts to the two-body density functions in EAM. The effectiveness of the new form is demonstrated using an extensive set of training data for tantalum structures. Similar to artificial neural network potentials, the quadratic SNAP form requires substantially more training data in order to prevent overfitting. The quality of this new potential form is measured through a robust cross-validation analysis. read less NOT USED (low confidence) R. Hu, “Random neural networks for dimensionality reduction and regularized supervised learning.” 2019. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: This dissertation explores Random Neural Networks (RNNs) in … read moreAbstract: This dissertation explores Random Neural Networks (RNNs) in several aspects and their applications. First, Novel RNNs have been proposed for dimensionality reduction and visualization. Based on Extreme Learning Machines (ELMs) and Self-Organizing Maps (SOMs) a new method is created to identify the important variables and visualize the data. This technique reduces the curse of dimensionality and improves furthermore the interpretability of the visualization and is tested on real nursing survey datasets. ELM-SOM+ is an autoencoder created to preserves the intrinsic quality of SOM and also brings continuity to the projection using two ELMs. This new methodology shows considerable improvement over SOM on real datasets. Second, as a Supervised Learning method, ELMs has been applied to the hierarchical multiscale method to bridge the the molecular dynamics to continua. The method is tested on simulation data and proven to be efficient for passing the information from one scale to another. Lastly, the regularization of ELMs has been studied and a new regularization algorithm for ELMs is created using a modified Lanczos Algorithm. The Lanczos ELM on average divide computational time by 20 and reduce the Normalized MSE by 14% comparing with regular ELMs. read less NOT USED (high confidence) A. Diggs et al., “Hydrogen-induced degradation dynamics in silicon heterojunction solar cells via machine learning,” Communications Materials. 2023. link Times cited: 1 NOT USED (high confidence) M. D. K. Jones, J. Dawson, S. Campbell, V. Barrioz, L. D. Whalley, and Y. Qu, “Modelling Interfaces in Thin-Film Photovoltaic Devices,” Frontiers in Chemistry. 2022. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: Developing effective device architectures for energy technol… read moreAbstract: Developing effective device architectures for energy technologies—such as solar cells, rechargeable batteries or fuel cells—does not only depend on the performance of a single material, but on the performance of multiple materials working together. A key part of this is understanding the behaviour at the interfaces between these materials. In the context of a solar cell, efficient charge transport across the interface is a pre-requisite for devices with high conversion efficiencies. There are several methods that can be used to simulate interfaces, each with an in-built set of approximations, limitations and length-scales. These methods range from those that consider only composition (e.g. data-driven approaches) to continuum device models (e.g. drift-diffusion models using the Poisson equation) and ab-initio atomistic models (developed using e.g. density functional theory). Here we present an introduction to interface models at various levels of theory, highlighting the capabilities and limitations of each. In addition, we discuss several of the various physical and chemical processes at a heterojunction interface, highlighting the complex nature of the problem and the challenges it presents for theory and simulation. read less NOT USED (high confidence) G. Baldinozzi and V. Pontikis, “Phenomenological potentials for the refractory metals Cr, Mo and W,” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 2022. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: Cohesion in the refractory metals Cr, Mo, and W is phenomeno… read moreAbstract: Cohesion in the refractory metals Cr, Mo, and W is phenomenologically described in this work via a n-body energy functional with a set of physically motivated parameters that were optimized to reproduce selected experimental properties characteristic of perfect and defective crystals. The functional contains four terms accounting for the hard-core repulsion, the Thomas–Fermi kinetic energy repulsion and for contributions to the binding energy of s and d valence electrons. Lattice dynamics, molecular statics, and molecular dynamics calculations show that this model describes satisfactorily thermodynamic properties of the studied metals whereas, unlike other empirical approaches from the literature, predictions of phonon dispersion relations and of surface and point defect energetics reveal in fair good agreement with experiments. These results suggest that the present model is well adapted to large-scale simulations and whenever total energy calculations of thermodynamic properties are unfeasible. read less NOT USED (high confidence) T. Lee et al., “Atomic-scale origin of the low grain-boundary resistance in perovskite solid electrolyte Li0.375Sr0.4375Ta0.75Zr0.25O3,” Nature Communications. 2022. link Times cited: 9 NOT USED (high confidence) H. Zheng et al., “Multi-scale investigation of short-range order and dislocation glide in MoNbTi and TaNbTi multi-principal element alloys,” npj Computational Materials. 2022. link Times cited: 8 NOT USED (high confidence) Y. Chen et al., “A Focused Review on Engineering Application of Multi-Principal Element Alloy,” Frontiers in Materials. 2022. link Times cited: 3 Abstract: Compared with traditional alloys with one principal componen… read moreAbstract: Compared with traditional alloys with one principal component up to 40–90%, multi-principal element alloys (MPEAs) were born in the complicated intermingling of traditional and non-traditional physical metallurgy, and brings us a great amount of excellent performances. Here, we would briefly summarize the potential applications in some key areas, which is helpful for latecomers to quickly and comprehensively understand this new alloy system. Especially, the applications of MPEAs in aerospace, industrial equipment, national defense, energy, navigation and so on are discussed roughly. Subsequently, several emerging areas have also been compared. Finally, some suggestions are given for the future development trend. read less NOT USED (high confidence) W. Zhang, S. Byna, H. Sim, S. Lee, S. S. Vazhkudai, and Y. Chen, “Exploiting User Activeness for Data Retention in HPC Systems,” SC21: International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis. 2021. link Times cited: 2 Abstract: HPC systems typically rely on the fixed-lifetime (FLT) data … read moreAbstract: HPC systems typically rely on the fixed-lifetime (FLT) data retention strategy, which only considers temporal locality of data accesses to parallel file systems. However, our extensive analysis based on the leadership-class HPC system traces suggests that the FLT approach often fails to capture the dynamics in users' behavior and leads to undesired data purge. In this study, we propose an activeness-based data retention (ActiveDR) solution, which advocates considering the data retention approach from a holistic activeness-based perspective. By evaluating the frequency and impact of users' activities, ActiveDR prioritizes the file purge process for inactive users and rewards active users with extended file lifetime on parallel storage. Our extensive evaluations based on the traces of the prior Titan supercomputer show that, when reaching the same purge target, ActiveDR achieves up to 37% file miss reduction as compared to the current FLT retention methodology. read less NOT USED (high confidence) R. Tamura, M. Matsuda, J. Lin, Y. Futamura, T. Sakurai, and T. Miyazaki, “Structural analysis based on unsupervised learning: Search for a characteristic low-dimensional space by local structures in atomistic simulations,” Physical Review B. 2021. link Times cited: 0 Abstract: Owing to the advances in computational techniques and the in… read moreAbstract: Owing to the advances in computational techniques and the increase in computational power, atomistic simulations of materials can simulate large systems with higher accuracy. Complex phenomena can be observed in such state-of-the-art atomistic simulations. However, it has become increasingly difficult to understand what is actually happening and mechanisms, for example, in molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. We propose an unsupervised machine learning method to analyze the local structure around a target atom. The proposed method, which uses the two-step locality preserving projections (TS-LPP), can find a low-dimensional space wherein the distributions of datapoints for each atom or groups of atoms can be properly captured. We demonstrate that the method is effective for analyzing the MD simulations of crystalline, liquid, and amorphous states and the melt-quench process from the perspective of local structures. The proposed method is demonstrated on a silicon single-component system, a silicon-germanium binary system, and a copper single-component system. read less NOT USED (high confidence) S. Moayedpour, D. Dardzinski, S. Yang, A. Hwang, and N. Marom, “Structure prediction of epitaxial inorganic interfaces by lattice and surface matching with Ogre.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2021. link Times cited: 8 Abstract: We present a new version of the Ogre open source Python pack… read moreAbstract: We present a new version of the Ogre open source Python package with the capability to perform structure prediction of epitaxial inorganic interfaces by lattice and surface matching. In the lattice matching step, a scan over combinations of substrate and film Miller indices is performed to identify the domain-matched interfaces with the lowest mismatch. Subsequently, surface matching is conducted by Bayesian optimization to find the optimal interfacial distance and in-plane registry between the substrate and the film. For the objective function, a geometric score function is proposed based on the overlap and empty space between atomic spheres at the interface. The score function reproduces the results of density functional theory (DFT) at a fraction of the computational cost. The optimized interfaces are pre-ranked using a score function based on the similarity of the atomic environment at the interface to the bulk environment. Final ranking of the top candidate structures is performed with DFT. Ogre streamlines DFT calculations of interface energies and electronic properties by automating the construction of interface models. The application of Ogre is demonstrated for two interfaces of interest for quantum computing and spintronics, Al/InAs and Fe/InSb. read less NOT USED (high confidence) J. Qi et al., “Bridging the gap between simulated and experimental ionic conductivities in lithium superionic conductors,” Materials Today Physics. 2021. link Times cited: 33 NOT USED (high confidence) Y. Mishin, “Machine-Learning Interatomic Potentials for Materials Science,” Electrical Engineering eJournal. 2021. link Times cited: 103 NOT USED (high confidence) Y.-S. Lin, G. P. P. Pun, and Y. Mishin, “Development of a physically-informed neural network interatomic potential for tantalum,” Computational Materials Science. 2021. link Times cited: 9 NOT USED (high confidence) G. P. P. Pun, V. Yamakov, J. Hickman, E. Glaessgen, and Y. Mishin, “Development of a general-purpose machine-learning interatomic potential for aluminum by the physically informed neural network method,” Physical Review Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 13 Abstract: Interatomic potentials constitute the key component of large… read moreAbstract: Interatomic potentials constitute the key component of large-scale atomistic simulations of materials. The recently proposed physically-informed neural network (PINN) method combines a high-dimensional regression implemented by an artificial neural network with a physics-based bond-order interatomic potential applicable to both metals and nonmetals. In this paper, we present a modified version of the PINN method that accelerates the potential training process and further improves the transferability of PINN potentials to unknown atomic environments. As an application, a modified PINN potential for Al has been developed by training on a large database of electronic structure calculations. The potential reproduces the reference first-principles energies within 2.6 meV per atom and accurately predicts a wide spectrum of physical properties of Al. Such properties include, but are not limited to, lattice dynamics, thermal expansion, energies of point and extended defects, the melting temperature, the structure and dynamic properties of liquid Al, the surface tensions of the liquid surface and the solid-liquid interface, and the nucleation and growth of a grain boundary crack. Computational efficiency of PINN potentials is also discussed. read less NOT USED (high confidence) J. Nigam, S. Pozdnyakov, and M. Ceriotti, “Recursive evaluation and iterative contraction of N-body equivariant features.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2020. link Times cited: 45 Abstract: Mapping an atomistic configuration to a symmetrized N-point … read moreAbstract: Mapping an atomistic configuration to a symmetrized N-point correlation of a field associated with the atomic positions (e.g., an atomic density) has emerged as an elegant and effective solution to represent structures as the input of machine-learning algorithms. While it has become clear that low-order density correlations do not provide a complete representation of an atomic environment, the exponential increase in the number of possible N-body invariants makes it difficult to design a concise and effective representation. We discuss how to exploit recursion relations between equivariant features of different order (generalizations of N-body invariants that provide a complete representation of the symmetries of improper rotations) to compute high-order terms efficiently. In combination with the automatic selection of the most expressive combination of features at each order, this approach provides a conceptual and practical framework to generate systematically improvable, symmetry adapted representations for atomistic machine learning. read less NOT USED (high confidence) J. Byggmastar, K. Nordlund, and F. Djurabekova, “Gaussian approximation potentials for body-centered-cubic transition metals,” Physical Review Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 22 Abstract: We develop a set of machine-learning interatomic potentials … read moreAbstract: We develop a set of machine-learning interatomic potentials for elemental V, Nb, Mo, Ta, and W using the Gaussian approximation potential framework. The potentials show good accuracy and transferability for elastic, thermal, liquid, defect, and surface properties. All potentials are augmented with accurate repulsive potentials, making them applicable to radiation damage simulations involving high-energy collisions. We study melting and liquid properties in detail and use the potentials to provide melting curves up to 400 GPa for all five elements. read less NOT USED (high confidence) C. Lapointe et al., “Machine learning surrogate models for prediction of point defect vibrational entropy,” Physical Review Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 5 Abstract: The temperature variation of the defect densities in a cryst… read moreAbstract: The temperature variation of the defect densities in a crystal depends on vibrational entropy. This contribution to the system thermodynamics remains computationally challenging as it requires a diagonalization of the system's Hessian which scales as $O({N}^{3})$ for a crystal made of $N$ atoms. Here, to circumvent such a heavy computational task and make it feasible even for systems containing millions of atoms, the harmonic vibrational entropy of point defects is estimated directly from the relaxed atomic positions through a linear-in-descriptor machine learning approach of order $O(N)$. With a size-independent descriptor dimension and fixed model parameters, an excellent predictive power is demonstrated on a wide range of defect configurations, supercell sizes, and external deformations well outside the training database. In particular, formation entropies in a range of $250{k}_{B}$ are predicted with less than $1.6{k}_{B}$ error from a training database whose formation entropies span only $25{k}_{B}$ (training error less than $1.0{k}_{B}$). This exceptional transferability is found to hold even when the training is limited to a low-energy superbasin in the phase space while the tests are performed for a different liquid-like superbasin at higher energies. read less NOT USED (high confidence) A. Tran, J. Tranchida, T. Wildey, and A. Thompson, “Multi-fidelity machine-learning with uncertainty quantification and Bayesian optimization for materials design: Application to ternary random alloys,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2020. link Times cited: 42 Abstract: We present a scale-bridging approach based on a multi-fideli… read moreAbstract: We present a scale-bridging approach based on a multi-fidelity (MF) machine-learning (ML) framework leveraging Gaussian processes (GP) to fuse atomistic computational model predictions across multiple levels of fidelity. Through the posterior variance of the MFGP, our framework naturally enables uncertainty quantification, providing estimates of confidence in the predictions. We used density functional theory as high-fidelity prediction, while a ML interatomic potential is used as low-fidelity prediction. Practical materials' design efficiency is demonstrated by reproducing the ternary composition dependence of a quantity of interest (bulk modulus) across the full aluminum-niobium-titanium ternary random alloy composition space. The MFGP is then coupled to a Bayesian optimization procedure, and the computational efficiency of this approach is demonstrated by performing an on-the-fly search for the global optimum of bulk modulus in the ternary composition space. The framework presented in this manuscript is the first application of MFGP to atomistic materials simulations fusing predictions between density functional theory and classical interatomic potential calculations. read less NOT USED (high confidence) D. Zagaceta, H. Yanxon, and Q. Zhu, “Spectral neural network potentials for binary alloys,” Journal of Applied Physics. 2020. link Times cited: 4 Abstract: In this work, we present a numerical implementation to compu… read moreAbstract: In this work, we present a numerical implementation to compute the atom centered descriptors introduced by Bartok et al (Phys. Rev. B, 87, 184115, 2013) based on the harmonic analysis of the atomic neighbor density function. Specifically, we focus on two types of descriptors, the smooth SO(3) power spectrum with the explicit inclusion of a radial basis and the SO(4) bispectrum obtained through mapping the radial component onto a polar angle of a four dimensional hypersphere. With these descriptors, various interatomic potentials for binary Ni-Mo alloys are obtained based on linear and neural network regression models. Numerical experiments suggest that both descriptors produce similar results in terms of accuracy. For linear regression, the smooth SO(3) power spectrum is superior to the SO(4) bispectrum when a large band limit is used. In neural network regression, a better accuracy can be achieved with even less number of expansion components for both descriptors. As such, we demonstrate that spectral neural network potentials are feasible choices for large scale atomistic simulation. read less NOT USED (high confidence) C. M. Andolina, P. Williamson, and W. Saidi, “Optimization and validation of a deep learning CuZr atomistic potential: Robust applications for crystalline and amorphous phases with near-DFT accuracy.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2020. link Times cited: 32 Abstract: We show that a deep-learning neural network potential (DP) b… read moreAbstract: We show that a deep-learning neural network potential (DP) based on density functional theory (DFT) calculations can well describe Cu-Zr materials, an example of a binary alloy system, that can coexist in as ordered intermetallic and as an amorphous phase. The complex phase diagram for Cu-Zr makes it a challenging system for traditional atomistic force-fields that cannot accurately describe the different properties and phases. Instead, we show that a DP approach using a large database with ∼300k configurations can render results generally on par with DFT. The training set includes configurations of pristine and bulk elementary metals and intermetallic structures in the liquid and solid phases in addition to slab and amorphous configurations. The DP model was validated by comparing bulk properties such as lattice constants, elastic constants, bulk moduli, phonon spectra, and surface energies to DFT values for identical structures. Furthermore, we contrast the DP results with values obtained using well-established two embedded atom method potentials. Overall, our DP potential provides near DFT accuracy for the different Cu-Zr phases but with a fraction of its computational cost, thus enabling accurate computations of realistic atomistic models, especially for the amorphous phase. read less NOT USED (high confidence) S. Desai, S. Reeve, and J. Belak, “Implementing a neural network interatomic model with performance portability for emerging exascale architectures,” Comput. Phys. Commun. 2020. link Times cited: 9 NOT USED (high confidence) C. Chen, Y. Zuo, W. Ye, X.-G. Li, Z. Deng, and S. Ong, “A Critical Review of Machine Learning of Energy Materials,” Advanced Energy Materials. 2020. link Times cited: 268 Abstract: Machine learning (ML) is rapidly revolutionizing many fields… read moreAbstract: Machine learning (ML) is rapidly revolutionizing many fields and is starting to change landscapes for physics and chemistry. With its ability to solve complex tasks autonomously, ML is being exploited as a radically new way to help find material correlations, understand materials chemistry, and accelerate the discovery of materials. Here, an in‐depth review of the application of ML to energy materials, including rechargeable alkali‐ion batteries, photovoltaics, catalysts, thermoelectrics, piezoelectrics, and superconductors, is presented. A conceptual framework is first provided for ML in materials science, with a broad overview of different ML techniques as well as best practices. This is followed by a critical discussion of how ML is applied in energy materials. This review is concluded with the perspectives on major challenges and opportunities in this exciting field. read less NOT USED (high confidence) X.-G. Li, C. Chen, H. Zheng, Y. Zuo, and S. Ong, “Complex strengthening mechanisms in the NbMoTaW multi-principal element alloy,” npj Computational Materials. 2019. link Times cited: 114 NOT USED (high confidence) T. Wen et al., “Development of a deep machine learning interatomic potential for metalloid-containing Pd-Si compounds,” Physical Review B. 2019. link Times cited: 30 Abstract: Interatomic potentials based on neural-network machine learn… read moreAbstract: Interatomic potentials based on neural-network machine learning (ML) approach to address the longstanding challenge of accuracy versus efficiency in molecular-dynamics simulations have recently attracted a great deal of interest. Here, utilizing Pd-Si system as a prototype, we extend the development of neural-network ML potentials to compounds exhibiting various types of bonding characteristics. The ML potential is trained by fitting to the energies and forces of both liquid and crystal structures firstprinciples calculations based on density-functional theory (DFT). We show that the generated ML potential captures the structural features and motifs in Pd82Si18 and Pd75Si25 liquids more accurately than the existing interatomic potential based on embedded-atom method (EAM). The ML potential also describes the solid-liquid interface of these systems very well. Moreover, while the existing EAM potential fails to describe the relative energies of various crystalline structures and predict wrong ground-state structures at Pd3Si and Pd9Si2 composition, the developed ML potential predicts correctly the groundstate structures from genetic algorithm search. The efficient ML potential with DFT accuracy from our study will provide a promising scheme for accurate atomistic simulations of structures and dynamics of complex Pd-Si system. Disciplines Condensed Matter Physics Authors Tongqi Wen, Cai-Zhuang Wang, Matthew J. Kramer, Yang Sun, Beilin Ye, Haidi Wang, Xueyuan Liu, Chao Zhang, Feng Zhang, Kai-Ming Ho, and Nan Wang This article is available at Iowa State University Digital Repository: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/ameslab_manuscripts/ 663 PHYSICAL REVIEW B 100, 174101 (2019) Development of a deep machine learning interatomic potential for metalloid-containing Pd-Si compounds Tongqi Wen ,1,2 Cai-Zhuang Wang,2,3,* M. J. Kramer ,2 Yang Sun ,2 Beilin Ye,4 Haidi Wang,2 Xueyuan Liu,2 Chao Zhang ,2,5 Feng Zhang,2 Kai-Ming Ho,2,3 and Nan Wang 1,† 1MOE Key Laboratory of Materials Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an 710072, China 2Ames Laboratory-USDOE, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa 50011, USA 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University, Ames, Iowa 50011, USA 4School of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510641, China 5Department of Physics, School of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology, Yantai University, Yantai, 264005, China (Received 16 July 2019; revised manuscript received 8 October 2019; published 4 November 2019) Interatomic potentials based on neural-network machine learning (ML) approach to address the long-standing challenge of accuracy versus efficiency in molecular-dynamics simulations have recently attracted a great deal of interest. Here, utilizing Pd-Si system as a prototype, we extend the development of neural-network ML potentials to compounds exhibiting various types of bonding characteristics. The ML potential is trained by fitting to the energies and forces of both liquid and crystal structures first-principles calculations based on density-functional theory (DFT). We show that the generated ML potential captures the structural features and motifs in Pd82Si18 and Pd75Si25 liquids more accurately than the existing interatomic potential based on embedded-atom method (EAM). The ML potential also describes the solid-liquid interface of these systems very well. Moreover, while the existing EAM potential fails to describe the relative energies of various crystalline structures and predict wrong ground-state structures at Pd3Si and Pd9Si2 composition, the developed ML potential predicts correctly the ground-state structures from genetic algorithm search. The efficient ML potential with DFT accuracy from our study will provide a promising scheme for accurate atomistic simulations of structures and dynamics of complex Pd-Si system. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevB.100.174101 read less NOT USED (high confidence) S. Xiao, R. Hu, Z. Li, S. Attarian, K.-M. Björk, and A. Lendasse, “A machine-learning-enhanced hierarchical multiscale method for bridging from molecular dynamics to continua,” Neural Computing and Applications. 2019. link Times cited: 17 NOT USED (high confidence) J. Schmidt, M. R. G. Marques, S. Botti, and M. A. L. Marques, “Recent advances and applications of machine learning in solid-state materials science,” npj Computational Materials. 2019. link Times cited: 1226 NOT USED (high confidence) H. Zheng et al., “Grain boundary properties of elemental metals,” Acta Materialia. 2019. link Times cited: 98 NOT USED (high confidence) S. Bishnoi et al., “Predicting Young’s modulus of oxide glasses with sparse datasets using machine learning,” Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids. 2019. link Times cited: 61 NOT USED (high confidence) M. Wood, M. Cusentino, B. Wirth, and A. Thompson, “Data-driven material models for atomistic simulation,” Physical Review B. 2019. link Times cited: 37 Abstract: The central approximation made in classical molecular dynami… read moreAbstract: The central approximation made in classical molecular dynamics simulation of materials is the interatomic potential used to calculate the forces on the atoms. Great effort and ingenuity is required to construct viable functional forms and find accurate parametrizations for potentials using traditional approaches. Machine learning has emerged as an effective alternative approach to develop accurate and robust interatomic potentials. Starting with a very general model form, the potential is learned directly from a database of electronic structure calculations and therefore can be viewed as a multiscale link between quantum and classical atomistic simulations. Risk of inaccurate extrapolation exists outside the narrow range of time and length scales where the two methods can be directly compared. In this work, we use the spectral neighbor analysis potential (SNAP) and show how a fit can be produced with minimal interpolation errors which is also robust in extrapolating beyond training. To demonstrate the method, we have developed a tungsten-beryllium potential suitable for the full range of binary compositions. Subsequently, large-scale molecular dynamics simulations were performed of high energy Be atom implantation onto the (001) surface of solid tungsten. The machine learned W-Be potential generates a population of implantation structures consistent with quantum calculations of defect formation energies. A very shallow ($l2\phantom{\rule{0.16em}{0ex}}\mathrm{nm}$) average Be implantation depth is predicted which may explain ITER diverter degradation in the presence of beryllium. read less NOT USED (high confidence) K. Butler, G. S. Gautam, and P. Canepa, “Designing interfaces in energy materials applications with first-principles calculations,” npj Computational Materials. 2019. link Times cited: 69 NOT USED (high confidence) Z. Deng, C. Chen, X.-G. Li, and S. Ong, “An electrostatic spectral neighbor analysis potential for lithium nitride,” npj Computational Materials. 2019. link Times cited: 62 NOT USED (high confidence) J. Wang, D. Shin, and S. Shin, “Comprehensive evaluation and parametric sensitivity of interatomic potential models for diffusion kinetics of Cr2O3 in molecular dynamics,” AIP Advances. 2019. link Times cited: 4 Abstract: While molecular dynamics (MD) has proven to be a promising a… read moreAbstract: While molecular dynamics (MD) has proven to be a promising approach to investigate the diffusion properties, the grand challenge resides in evaluating potential model parameters to accurately replicate experimentally measured properties. The Buckingham potential model with Columbic interaction is widely employed in MD simulations of chromia (Cr2O3) systems, as it allows for reasonable computational cost and accuracy. However, considering the well-known limitation of classical potential models in simultaneous reproduction of various physical phenomena, further comprehensive evaluation of the potential is required for calculation of diffusion properties. In this study, we benchmark the performance of three different Buckingham models with the experimental data by calculating structural, thermodynamic, and mechanical properties of defect-free Cr2O3, and diffusion properties of Cr2O3 with vacancy defects. Available Buckingham models display limited accuracies, consolidating the necessity of retraining the potential parameters for all properties impacting the diffusion dynamics. Oversimplification in parameterization procedures is suggested to impede the universal performance in property reproduction. This research also demonstrates effective guidelines for choosing a proper parameter set of current Buckingham potential for MD simulation with Cr2O3 depending on properties and for potential reparameterization. read less NOT USED (high confidence) A. Seko, A. Togo, and I. Tanaka, “Group-theoretical high-order rotational invariants for structural representations: Application to linearized machine learning interatomic potential,” Physical Review B. 2019. link Times cited: 22 Abstract: Many rotational invariants for crystal structure representat… read moreAbstract: Many rotational invariants for crystal structure representations have been used to describe the structure-property relationship by machine learning. The machine learning interatomic potential (MLIP) is one of the applications of rotational invariants, which provides the relationship between the energy and the crystal structure. Since the MLIP requires the highest accuracy among machine learning estimations of the structure-property relationship, the enumeration of rotational invariants is useful for constructing MLIPs with the desired accuracy. In this study, we introduce high-order linearly independent rotational invariants up to the sixth order based on spherical harmonics and apply them to linearized MLIPs for elemental aluminum. A set of rotational invariants is derived by the general process of reducing the Kronecker products of irreducible representations (Irreps) for the SO(3) group using a group-theoretical projector method. A high predictive power for a wide range of structures is accomplished by using high-order invariants with low-order invariants equivalent to pair and angular structural features. read less NOT USED (high confidence) S. A. Miller, M. Dylla, S. Anand, K. Gordiz, G. J. Snyder, and E. Toberer, “Empirical modeling of dopability in diamond-like semiconductors,” npj Computational Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 17 NOT USED (high confidence) S. Xiao, A. Lendasse, and R. Hu, “Data-Enabled Computational Multiscale Method in Materials Science and Engineering,” 2018 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI). 2018. link Times cited: 1 Abstract: In the community of computational materials science, one of … read moreAbstract: In the community of computational materials science, one of the challenges in hierarchical multiscale modeling is information-passing from one scale to another, especially from the molecular model to the continuum model. A machine-learning-enhanced approach, proposed in this paper, provides an alternative solution. In the developed hierarchical multiscale method, molecular dynamics simulations in the molecular model are conducted first to generate datasets, which represents physical phenomena at the nanoscale. The datasets are then used to train neural networks for failure classification and stress regressions. Finally, the well-trained learning machines are implemented in the continuum model to study the mechanical behaviors of materials at the macroscale. Randomized neural networks are employed due to their computational efficiency. read less NOT USED (high confidence) W. Ye, C. Chen, S. Dwaraknath, A. Jain, S. Ong, and K. Persson, “Harnessing the Materials Project for machine-learning and accelerated discovery,” MRS Bulletin. 2018. link Times cited: 21 Abstract: Improvements in computational resources over the last decade… read moreAbstract: Improvements in computational resources over the last decade are enabling a new era of computational prediction and design of novel materials. The resulting resources are databases such as the Materials Project (www.materialsproject.org), which is harnessing the power of supercomputing together with state-of-the-art quantum mechanical theory to compute the properties of all known inorganic materials, to design novel materials, and to make the data available for free to the community, together with online analysis and design algorithms. The current release contains data derived from quantum mechanical calculations for more than 70,000 materials and millions of associated materials properties. The software infrastructure carries out thousands of calculations per week, enabling screening and predictions for both novel solids as well as molecular species with targeted properties. As the rapid growth of accessible computed materials properties continues, the next frontier is harnessing that information for automated learning and accelerated discovery. In this article, we highlight some of the emerging and exciting efforts, and successes, as well as current challenges using descriptor-based and machine-learning methods for data-accelerated materials design. read less NOT USED (high confidence) X.-G. Li, C. Hu, C. Chen, Z. Deng, J. Luo, and S. Ong, “Quantum-accurate spectral neighbor analysis potential models for Ni-Mo binary alloys and fcc metals,” Physical Review B. 2018. link Times cited: 61 Abstract: In recent years, efficient interatomic potentials approachin… read moreAbstract: In recent years, efficient interatomic potentials approaching the accuracy of density functional theory (DFT) calculations have been developed using rigorous atomic descriptors satisfying strict invariances, for example, for translation, rotation, permutation of homonuclear atoms, among others. In this paper, we generalize the spectral neighbor analysis potential (SNAP) model to bcc-fcc binary alloy systems. We demonstrate that machine-learned SNAP models can yield significant improvements even over the well-established high-performing embedded atom method (EAM) and modified EAM potentials for fcc Cu and Ni. We also report on the development of a SNAP model for the fcc Ni-bcc Mo binary system by machine learning a carefully constructed large computed data set of elemental and intermetallic compounds. We demonstrate that this binary Ni-Mo SNAP model can achieve excellent agreement with experiments in the prediction of a Ni-Mo phase diagram as well as near-DFT accuracy in the prediction of many key properties, such as elastic constants, formation energies, melting points, etc., across the entire binary composition range. In contrast, the existing Ni-Mo EAM has significant errors in the prediction of the phase diagram and completely fails in binary compounds. This paper provides a systematic model development process for multicomponent alloy systems, including an efficient procedure to optimize the hyperparameters in the model fitting, and paves the way for long-time large-scale simulations of such systems. read less NOT USED (high confidence) Q. Bai, L. Yang, H. Chen, and Y. Mo, “Computational Studies of Electrode Materials in Sodium‐Ion Batteries,” Advanced Energy Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 120 Abstract: Sodium‐ion batteries have attracted extensive interest as a … read moreAbstract: Sodium‐ion batteries have attracted extensive interest as a promising solution for large‐scale electrochemical energy storage, owing to their low cost, materials abundance, good reversibility, and decent energy density. For sodium‐ion batteries to achieve comparable performance to current lithium‐ion batteries, significant improvements are still required in cathode, anode, and electrolyte materials. Understanding the functioning and degradation mechanisms of the materials is essential. Computational techniques have been widely applied in tandem with experimental investigations to provide crucial fundamental insights into electrode materials and to facilitate the development of materials for sodium‐ion batteries. Herein, the authors review computational studies on electrode materials in sodium‐ion batteries. The authors summarize the current state‐of‐the‐art computational techniques and their applications in investigating the structure, ordering, diffusion, and phase transformation in cathode and anode materials for sodium‐ion batteries. The unique capability and the obtained knowledge of computational studies as well as the perspectives for sodium‐ion battery materials are discussed in this review. read less NOT USED (high confidence) Y. Zhang and C. Ling, “A strategy to apply machine learning to small datasets in materials science,” npj Computational Materials. 2018. link Times cited: 406 NOT USED (high confidence) A. Bartók, J. Kermode, N. Bernstein, and G. Csányi, “Machine Learning a General-Purpose Interatomic Potential for Silicon,” Physical Review X. 2018. link Times cited: 291 Abstract: The success of first principles electronic structure calcula… read moreAbstract: The success of first principles electronic structure calculation for predictive modeling in chemistry, solid state physics, and materials science is constrained by the limitations on simulated length and time scales due to computational cost and its scaling. Techniques based on machine learning ideas for interpolating the Born-Oppenheimer potential energy surface without explicitly describing electrons have recently shown great promise, but accurately and efficiently fitting the physically relevant space of configurations has remained a challenging goal. Here we present a Gaussian Approximation Potential for silicon that achieves this milestone, accurately reproducing density functional theory reference results for a wide range of observable properties, including crystal, liquid, and amorphous bulk phases, as well as point, line, and plane defects. We demonstrate that this new potential enables calculations that would be extremely expensive with a first principles electronic structure method, such as finite temperature phase boundary lines, self-diffusivity in the liquid, formation of the amorphous by slow quench, and dynamic brittle fracture. We show that the uncertainty quantification inherent to the Gaussian process regression framework gives a qualitative estimate of the potential's accuracy for a given atomic configuration. The success of this model shows that it is indeed possible to create a useful machine-learning-based interatomic potential that comprehensively describes a material, and serves as a template for the development of such models in the future. read less NOT USED (high confidence) A. Takahashi, A. Seko, and I. Tanaka, “Linearized machine-learning interatomic potentials for non-magnetic elemental metals: Limitation of pairwise descriptors and trend of predictive power.,” The Journal of chemical physics. 2017. link Times cited: 20 Abstract: Machine-learning interatomic potential (MLIP) has been of gr… read moreAbstract: Machine-learning interatomic potential (MLIP) has been of growing interest as a useful method to describe the energetics of systems of interest. In the present study, we examine the accuracy of linearized pairwise MLIPs and angular-dependent MLIPs for 31 elemental metals. Using all of the optimal MLIPs for 31 elemental metals, we show the robustness of the linearized frameworks, the general trend of the predictive power of MLIPs, and the limitation of pairwise MLIPs. As a result, we obtain accurate MLIPs for all 31 elements using the same linearized framework. This indicates that the use of numerous descriptors is the most important practical feature for constructing MLIPs with high accuracy. An accurate MLIP can be constructed using only pairwise descriptors for most non-transition metals, whereas it is very important to consider angular-dependent descriptors when expressing interatomic interactions of transition metals. read less NOT USED (high confidence) D. Dragoni, T. Daff, G. Csányi, and N. Marzari, “Achieving DFT accuracy with a machine-learning interatomic potential: thermomechanics and defects in bcc ferromagnetic iron,” arXiv: Materials Science. 2017. link Times cited: 167 Abstract: We show that the Gaussian Approximation Potential machine le… read moreAbstract: We show that the Gaussian Approximation Potential machine learning framework can describe complex magnetic potential energy surfaces, taking ferromagnetic iron as a paradigmatic challenging case. The training database includes total energies, forces, and stresses obtained from density-functional theory in the generalized-gradient approximation, and comprises approximately 150,000 local atomic environments, ranging from pristine and defected bulk configurations to surfaces and generalized stacking faults with different crystallographic orientations. We find the structural, vibrational and thermodynamic properties of the GAP model to be in excellent agreement with those obtained directly from first-principles electronic-structure calculations. There is good transferability to quantities, such as Peierls energy barriers, which are determined to a large extent by atomic configurations that were not part of the training set. We observe the benefit and the need of using highly converged electronic-structure calculations to sample a target potential energy surface. The end result is a systematically improvable potential that can achieve the same accuracy of density-functional theory calculations, but at a fraction of the computational cost. read less NOT USED (high confidence) Y. Yang et al., “Taking materials dynamics to new extremes using machine learning interatomic potentials,” Journal of Materials Informatics. 2021. link Times cited: 5 Abstract: Understanding materials dynamics under extreme conditions of… read moreAbstract: Understanding materials dynamics under extreme conditions of pressure, temperature, and strain rate is a scientific quest that spans nearly a century. Atomic simulations have had a considerable impact on this endeavor because of their ability to uncover materials’ microstructure evolution and properties at the scale of the relevant physical phenomena. However, this is still a challenge for most materials as it requires modeling large atomic systems (up to millions of particles) with improved accuracy. In many cases, the availability of sufficiently accurate but efficient interatomic potentials has become a serious bottleneck for performing these simulations as traditional potentials fail to represent the multitude of bonding. A new class of potentials has emerged recently, based on a different paradigm from the traditional approach. The new potentials are constructed by machinelearning with a high degree of fidelity from quantum-mechanical calculations. In this review, a brief introduction to the central ideas underlying machine learning interatomic potentials is given. In particular, the coupling of machine learning models with domain knowledge to improve accuracy, computational efficiency, and interpretability is highlighted. Subsequently, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the domain knowledge-based approach in certain select problems related to the kinetic response of warm dense materials. It is hoped that this review will inspire further advances in the understanding of matter under extreme conditions. read less |
 SNAP_ChenDengTran_2017_Mo__MO_698578166685_000
SNAP_ChenDengTran_2017_Mo__MO_698578166685_000