Sim_LAMMPS_ReaxFF_AryanpourVanDuinKubicki_2010_FeHO__SM_222964216001_000
| Title
A single sentence description.
|
LAMMPS ReaxFF potential for Fe-H-O systems developed by Aryanpour, van Duin, and Kubicki (2010) v000 |
|---|---|
| Description | LAMMPS ReaxFF potential for Fe-H-O systems ('pair_style reax/c' with potential file ffield.reax.Fe_O_C_H and additional control and charge equilibration information). The initial force field parameters for the Fe-Fe parameters were taken from an earlier force field development project on bulk-iron metal, based on DFT-calculations on antiferromagnetic BCC and FCC. The DFT data can be found in Ref 31 of the above-mentioned manuscript. The O/H parameters were taken from the ReaxFF bulk water description. The Fe/Fe and O/H parameters were kept fixed to these initial values, whereas the Fe/O parameters were reoptimized against the quantum mechanical results presented in the above-mentioned manuscript. |
| Species
The supported atomic species.
| Fe, H, O |
| Disclaimer
A statement of applicability provided by the contributor, informing users of the intended use of this KIM Item.
|
None |
| Content Origin | LAMMPS package 29-Feb-2019 |
| Contributor |
Ellad B. Tadmor |
| Maintainer |
Ellad B. Tadmor |
| Published on KIM | 2019 |
| How to Cite | Click here to download this citation in BibTeX format. |
| Funding | Not available |
| Short KIM ID
The unique KIM identifier code.
| SM_222964216001_000 |
| Extended KIM ID
The long form of the KIM ID including a human readable prefix (100 characters max), two underscores, and the Short KIM ID. Extended KIM IDs can only contain alpha-numeric characters (letters and digits) and underscores and must begin with a letter.
| Sim_LAMMPS_ReaxFF_AryanpourVanDuinKubicki_2010_FeHO__SM_222964216001_000 |
| DOI |
10.25950/66db8e67 https://doi.org/10.25950/66db8e67 https://commons.datacite.org/doi.org/10.25950/66db8e67 |
| KIM Item Type | Simulator Model |
| KIM API Version | 2.1 |
| Simulator Name
The name of the simulator as defined in kimspec.edn.
| LAMMPS |
| Potential Type | reax |
| Simulator Potential | reax/c |
| Grade | Name | Category | Brief Description | Full Results | Aux File(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | vc-species-supported-as-stated | mandatory | The model supports all species it claims to support; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-periodicity-support | mandatory | Periodic boundary conditions are handled correctly; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-permutation-symmetry | mandatory | Total energy and forces are unchanged when swapping atoms of the same species; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-forces-numerical-derivative | consistency | Forces computed by the model agree with numerical derivatives of the energy; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-dimer-continuity-c1 | informational | The energy versus separation relation of a pair of atoms is C1 continuous (i.e. the function and its first derivative are continuous); see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-objectivity | informational | Total energy is unchanged and forces transform correctly under rigid-body translation and rotation; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| F | vc-inversion-symmetry | informational | Total energy is unchanged and forces change sign when inverting a configuration through the origin; see full description. |
Results | Files |
| P | vc-memory-leak | informational | The model code does not have memory leaks (i.e. it releases all allocated memory at the end); see full description. |
Results | Files |
| N/A | vc-thread-safe | mandatory | The model returns the same energy and forces when computed in serial and when using parallel threads for a set of configurations. Note that this is not a guarantee of thread safety; see full description. |
Results | Files |
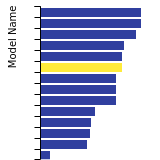
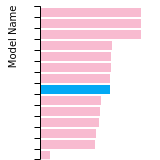
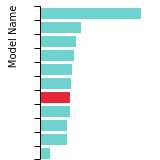
BCC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic body-centered cubic (bcc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
Cohesive Energy Graph
This graph shows the cohesive energy versus volume-per-atom for the current mode for four mono-atomic cubic phases (body-centered cubic (bcc), face-centered cubic (fcc), simple cubic (sc), and diamond). The curve with the lowest minimum is the ground state of the crystal if stable. (The crystal structure is enforced in these calculations, so the phase may not be stable.) Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
(No matching species)Diamond Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered diamond lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
Dislocation Core Energies
This graph shows the dislocation core energy of a cubic crystal at zero temperature and pressure for a specific set of dislocation core cutoff radii. After obtaining the total energy of the system from conjugate gradient minimizations, non-singular, isotropic and anisotropic elasticity are applied to obtain the dislocation core energy for each of these supercells with different dipole distances. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
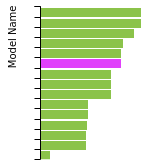
(No matching species)FCC Elastic Constants
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) elastic constants predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
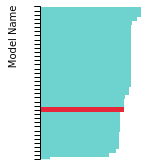
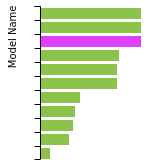
(No matching species)FCC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in red) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
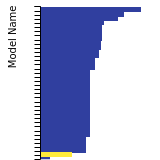
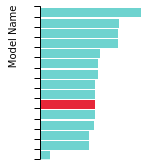
FCC Stacking Fault Energies
This bar chart plot shows the intrinsic and extrinsic stacking fault energies as well as the unstable stacking and unstable twinning energies for face-centered cubic (fcc) predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
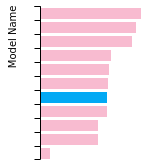
(No matching species)FCC Surface Energies
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic face-centered cubic (fcc) relaxed surface energies predicted by the current model (shown in blue) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
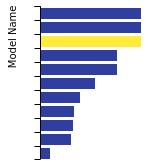
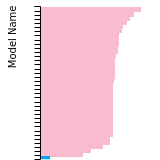
(No matching species)SC Lattice Constant
This bar chart plot shows the mono-atomic simple cubic (sc) lattice constant predicted by the current model (shown in the unique color) compared with the predictions for all other models in the OpenKIM Repository that support the species. The vertical bars show the average and standard deviation (one sigma) bounds for all model predictions. Graphs are generated for each species supported by the model.
Cubic Crystal Basic Properties Table
Species: FeSpecies: H
Species: O
Creators: Brandon Runnels
Contributor: brunnels
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/4723cee7
Computes grain boundary energy for a range of tilt angles given a crystal structure, tilt axis, and material.
| Test | Test Results | Link to Test Results page | Benchmark time
Usertime multiplied by the Whetstone Benchmark. This number can be used (approximately) to compare the performance of different models independently of the architecture on which the test was run.
Measured in Millions of Whetstone Instructions (MWI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 100 symmetric tilt grain boundary in bcc Fe v000 | view | 127093685 | |
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 110 symmetric tilt grain boundary in bcc Fe v000 | view | 303092247 | |
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 111 symmetric tilt grain boundary in bcc Fe v000 | view | 157556283 | |
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 112 symmetric tilt grain boundary in bcc Fe v000 | view | 648669165 | |
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 100 symmetric tilt grain boundary in fcc Fe v000 | view | 661317024 |
Creators: Daniel S. Karls and Junhao Li
Contributor: karls
Publication Year: 2019
DOI: https://doi.org/10.25950/2765e3bf
Equilibrium lattice constant and cohesive energy of a cubic lattice at zero temperature and pressure.
| Test | Error Categories | Link to Error page |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxed energy as a function of tilt angle for a 110 symmetric tilt grain boundary in fcc Fe v000 | other | view |
LatticeConstantCubicEnergy__TD_475411767977_007
| Test | Error Categories | Link to Error page |
|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium zero-temperature lattice constant for sc Fe v007 | other | view |
LatticeConstantHexagonalEnergy__TD_942334626465_005
| Test | Error Categories | Link to Error page |
|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp Fe v005 | other | view |
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp H v005 | other | view |
| Equilibrium lattice constants for hcp O v005 | other | view |
No Driver
| Verification Check | Error Categories | Link to Error page |
|---|---|---|
| MemoryLeak__VC_561022993723_001 | other | view |
| ThreadSafety__VC_881176209980_001 | other | view |
| Sim_LAMMPS_ReaxFF_AryanpourVanDuinKubicki_2010_FeHO__SM_222964216001_000.txz | Tar+XZ | Linux and OS X archive |
| Sim_LAMMPS_ReaxFF_AryanpourVanDuinKubicki_2010_FeHO__SM_222964216001_000.zip | Zip | Windows archive |